本讨论扩展了 Servlet 安全性:大图,以描述 Spring Security 在 Servlet 身份验证中使用的主要架构组件。 如果需要具体的流程来解释这些部分如何组合在一起,请查看身份验证机制特定部分。
-
SecurityContextHolder - Spring Security 存储身份验证人员的详细信息。
SecurityContextHolder -
SecurityContext - 从当前经过身份验证的用户中获取并包含其。
SecurityContextHolderAuthentication -
身份验证 - 可以是用于提供用户提供的用于身份验证的凭据的输入,也可以是当前用户从 .
AuthenticationManagerSecurityContext -
GrantedAuthority - 授予主体的权限(即角色、作用域等)
Authentication -
AuthenticationManager - 定义 Spring Security 过滤器如何执行身份验证的 API。
-
ProviderManager - 最常见的实现。
AuthenticationManager -
AuthenticationProvider - 用于执行特定类型的身份验证。
ProviderManager -
使用
AuthenticationEntryPoint请求凭据 - 用于从客户端请求凭据(即重定向到登录页面、发送响应等)WWW-Authenticate -
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter - 用于身份验证的基。 这也很好地了解了身份验证的高级流程以及各个部分如何协同工作。
Filter
SecurityContextHolder
Spring Security 身份验证模型的核心是 .
它包含 SecurityContext。SecurityContextHolder

这是 Spring Security 存储身份验证人员的详细信息的地方。
Spring Security 不关心如何填充。
如果它包含一个值,则将其用作当前经过身份验证的用户。SecurityContextHolderSecurityContextHolder
指示用户已通过身份验证的最简单方法是直接设置:SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder-
Java
-
Kotlin
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext(); (1)
Authentication authentication =
new TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER"); (2)
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context); (3)val context: SecurityContext = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext() (1)
val authentication: Authentication = TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER") (2)
context.authentication = authentication
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context) (3)| 1 | 我们首先创建一个空的 .
您应该创建一个新实例,而不是用于避免跨多个线程的争用条件。SecurityContextSecurityContextSecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication) |
| 2 | 接下来,我们创建一个新的 Authentication 对象。
Spring Security 不关心在 .
在这里,我们使用 ,因为它非常简单。
更常见的生产方案是 。AuthenticationSecurityContextTestingAuthenticationTokenUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, password, authorities) |
| 3 | 最后,我们将 on 设置为 .
Spring Security 使用此信息进行授权。SecurityContextSecurityContextHolder |
要获取有关经过身份验证的主体的信息,请访问 .SecurityContextHolder
-
Java
-
Kotlin
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
String username = authentication.getName();
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();val context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
val authentication = context.authentication
val username = authentication.name
val principal = authentication.principal
val authorities = authentication.authorities默认情况下,使用 a 来存储这些详细信息,这意味着 始终可用于同一线程中的方法来,即使 没有显式传递为这些方法的参数。
以这种方式使用 a 是非常安全的,如果你在处理当前主体的请求后注意清除线程。
Spring Security 的 FilterChainProxy 确保始终清除。SecurityContextHolderThreadLocalSecurityContextSecurityContextThreadLocalSecurityContext
某些应用程序并不完全适合使用 ,因为它们使用线程的特定方式。
例如,Swing 客户端可能希望 Java 虚拟机中的所有线程都使用相同的安全上下文。
您可以在启动时使用策略进行配置,以指定您希望如何存储上下文。
对于独立应用程序,您将使用该策略。
其他应用程序可能希望由安全线程生成的线程也采用相同的安全标识。
您可以通过使用 来实现此目的。
您可以通过两种方式从默认模式更改模式。
首先是设置系统属性。
第二种是在 上调用静态方法。
大多数应用程序不需要从默认值更改。
但是,如果您这样做,请查看 JavaDoc 以了解更多信息。ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderSecurityContextHolder.MODE_GLOBALSecurityContextHolder.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCALSecurityContextHolder.MODE_THREADLOCALSecurityContextHolderSecurityContextHolder
| 1 | 我们首先创建一个空的 .
您应该创建一个新实例,而不是用于避免跨多个线程的争用条件。SecurityContextSecurityContextSecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication) |
| 2 | 接下来,我们创建一个新的 Authentication 对象。
Spring Security 不关心在 .
在这里,我们使用 ,因为它非常简单。
更常见的生产方案是 。AuthenticationSecurityContextTestingAuthenticationTokenUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, password, authorities) |
| 3 | 最后,我们将 on 设置为 .
Spring Security 使用此信息进行授权。SecurityContextSecurityContextHolder |
安全上下文
SecurityContext 是从 SecurityContextHolder 获取的。
包含一个 Authentication 对象。SecurityContext
认证
身份验证界面在 Spring Security 中有两个主要用途:
-
AuthenticationManager的输入,用于提供用户提供的用于身份验证的凭据。 在此方案中使用时,返回 。isAuthenticated()false -
表示当前经过身份验证的用户。 您可以从 SecurityContext 获取电流。
Authentication
包含:Authentication
-
principal:标识用户。 使用用户名/密码进行身份验证时,这通常是UserDetails的实例。 -
credentials:通常是密码。 在许多情况下,在用户通过身份验证后会清除此漏洞,以确保它不会泄露。 -
authorities:GrantedAuthority实例是授予用户的高级权限。 两个示例是角色和作用域。
授予权限
GrantedAuthority 实例是授予用户的高级权限。
两个示例是角色和作用域。
您可以从 Authentication.getAuthorities() 方法获取实例。
此方法提供 of 对象。
毫不奇怪,A 是授予委托人的权力。
这种权限通常是“角色”,例如 或 。
稍后将针对 Web 授权、方法授权和域对象授权配置这些角色。
Spring Security 的其他部分会解释这些权限,并期望它们在场。
使用用户名/密码时,基于用户名/密码的身份验证实例通常由 UserDetailsService 加载。GrantedAuthorityCollectionGrantedAuthorityGrantedAuthorityROLE_ADMINISTRATORROLE_HR_SUPERVISORGrantedAuthority
通常,这些对象是应用程序范围的权限。
它们不特定于给定的域对象。
因此,您不太可能具有对对象编号 54 的权限表示权限,因为如果有数千个这样的权限,您将很快耗尽内存(或者至少会导致应用程序需要很长时间来验证用户身份)。
当然,Spring Security 是专门为处理这个常见需求而设计的,但你应该为此目的使用项目的域对象安全功能。GrantedAuthorityGrantedAuthorityEmployee
AuthenticationManager(身份验证管理器)
AuthenticationManager 是定义 Spring Security 过滤器如何执行身份验证的 API。
然后,返回的身份验证由调用 .
如果您不与 Spring Security 的实例集成,则可以直接设置 ,并且不需要使用 .AuthenticationManagerFiltersSecurityContextHolderAuthenticationManager
虽然实现可以是任何东西,但最常见的实现是 ProviderManager。AuthenticationManager
ProviderManager
ProviderManager 是 AuthenticationManager 最常用的实现。 委托给 AuthenticationProvider 实例。
每个都有机会指示身份验证应该成功、失败,或者指示它无法做出决定并允许下游做出决定。
如果配置的实例都无法进行身份验证,则身份验证将失败,并显示 ,这是一个特殊实例,指示未配置为支持传递到其中的实例的类型。ProviderManagerListAuthenticationProviderAuthenticationProviderAuthenticationProviderProviderNotFoundExceptionAuthenticationExceptionProviderManagerAuthentication
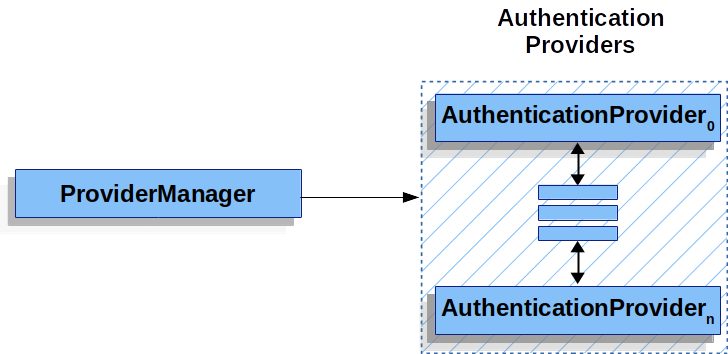
在实践中,每个人都知道如何执行特定类型的身份验证。
例如,一个可能能够验证用户名/密码,而另一个可能能够验证 SAML 断言。
这允许每个 Bean 执行非常特定类型的身份验证,同时支持多种类型的身份验证,并且只公开单个 Bean。AuthenticationProviderAuthenticationProviderAuthenticationProviderAuthenticationManager
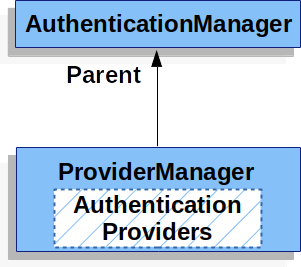
ProviderManager还允许配置可选的父级,如果无法执行身份验证,则会查阅该父级。
父级可以是 的任何类型,但它通常是 的实例。AuthenticationManagerAuthenticationProviderAuthenticationManagerProviderManager
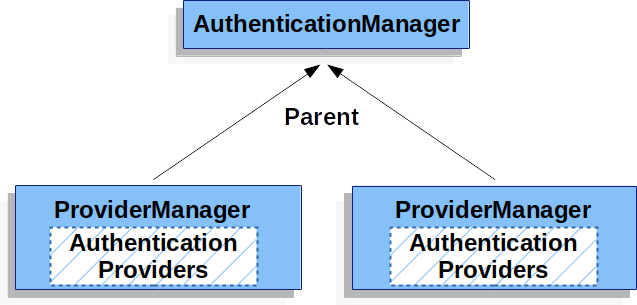
事实上,多个实例可能共享同一个父级。
这在有多个 SecurityFilterChain 实例的情况下很常见,这些实例具有一些共同的身份验证(共享父级),但也具有不同的身份验证机制(不同的实例)。ProviderManagerAuthenticationManagerAuthenticationManagerProviderManager
默认情况下,尝试从成功身份验证请求返回的对象中清除任何敏感凭据信息。
这样可以防止信息(如密码)在 .ProviderManagerAuthenticationHttpSession
当您使用用户对象的缓存时,这可能会导致问题,例如,在无状态应用程序中提高性能。
如果 包含对缓存中对象(如实例)的引用,并且删除了其凭据,则无法再对缓存的值进行身份验证。
如果使用缓存,则需要考虑到这一点。
一个明显的解决方案是首先在缓存实现或创建返回对象的实现中创建对象的副本。
或者,您可以禁用 上的属性。
请参阅 ProviderManager 类的 Javadoc。AuthenticationUserDetailsAuthenticationProviderAuthenticationeraseCredentialsAfterAuthenticationProviderManager
AuthenticationProvider
您可以将多个 AuthenticationProvider实例注入到 ProviderManager 中。
每个都执行特定类型的身份验证。
例如,DaoAuthenticationProvider 支持基于用户名/密码的身份验证,同时支持对 JWT 令牌进行身份验证。AuthenticationProviderJwtAuthenticationProvider
请求凭据AuthenticationEntryPoint
AuthenticationEntryPoint 用于发送从客户端请求凭据的 HTTP 响应。
有时,客户端会主动包含凭据(例如用户名和密码)来请求资源。 在这些情况下,Spring Security 不需要提供从客户端请求凭据的 HTTP 响应,因为它们已经包含在内。
在其他情况下,客户端会向他们无权访问的资源发出未经身份验证的请求。
在本例中,使用 的实现从客户端请求凭据。
实现可能会执行重定向到登录页面、使用 WWW-Authenticate 标头进行响应或执行其他操作。AuthenticationEntryPointAuthenticationEntryPoint
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 用作对用户凭据进行身份验证的基础。
在对凭据进行身份验证之前,Spring Security 通常使用 AuthenticationEntryPoint 请求凭据。Filter
接下来,可以对提交给它的任何身份验证请求进行身份验证。AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter

![]() 当用户提交其凭据时,将从要进行身份验证的
当用户提交其凭据时,将从要进行身份验证的 Authentication 创建身份验证。
创建的类型取决于 的子类。
例如,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 从在 . AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilterHttpServletRequestAuthenticationAbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilterUsernamePasswordAuthenticationTokenHttpServletRequest
![]() 接下来,
接下来,将身份验证传递到 AuthenticationManager 中进行身份验证。
![]() 如果身份验证失败,则为失败。
如果身份验证失败,则为失败。
-
RememberMeServices.loginFail被调用。 如果未配置“记住我”,则这是无操作的。 请参阅rememberme包。 -
AuthenticationFailureHandler被调用。 请参阅AuthenticationFailureHandler接口。
![]() 如果身份验证成功,则为成功。
如果身份验证成功,则为成功。
-
SessionAuthenticationStrategy收到新登录通知。 请参阅SessionAuthenticationStrategy接口。 -
身份验证是在 SecurityContextHolder 上设置的。 稍后,如果需要保存 以便可以在将来的请求中自动设置它,则必须显式调用。 请参见
SecurityContextHolderFilter类。SecurityContextSecurityContextRepository#saveContext -
RememberMeServices.loginSuccess被调用。 如果未配置“记住我”,则这是无操作的。 请参阅rememberme包。 -
ApplicationEventPublisher发布 .InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent -
AuthenticationSuccessHandler被调用。 请参阅AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口。