|
对于最新的稳定版本,请使用 spring-cloud-contract 4.2.0! |
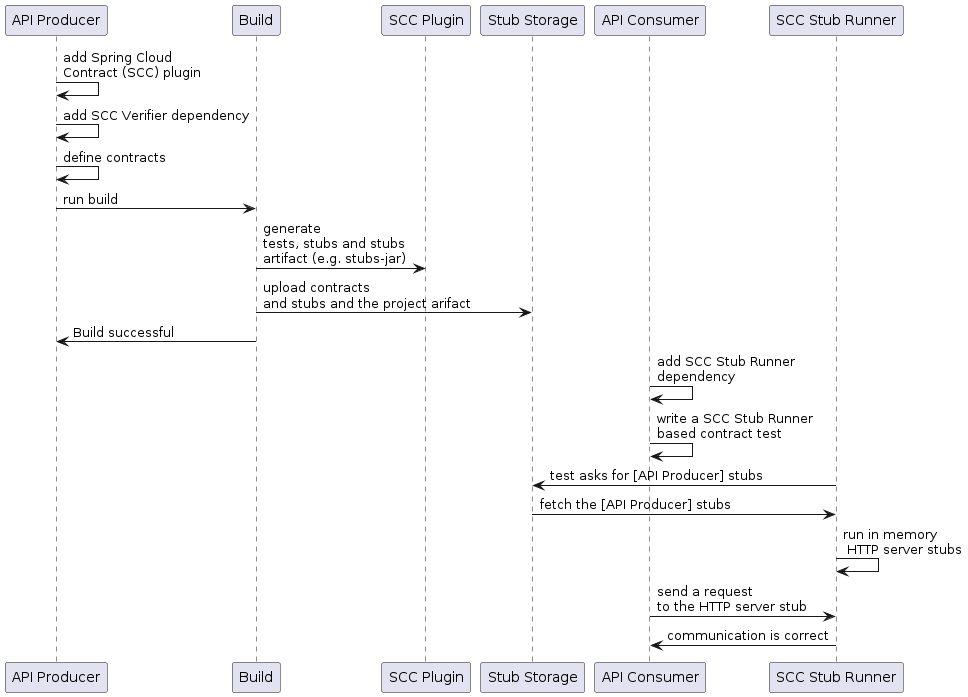
开发您的第一个基于 Contract 的 Spring Cloud 应用程序
在生产者端
开始使用Spring Cloud Contract中,您可以添加 Spring Cloud Contract Verifier
dependency 和 plugin 添加到您的构建文件中,如下例所示:
下面的清单显示了如何添加插件,它应该放在 build/plugins 中 部分:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
</plugin>|
最简单的入门方法是转到 Spring Initializr 并添加 “Web” 和 “Contract Verifier” 作为依赖项。这样做会引入以前的
提到的依赖项以及 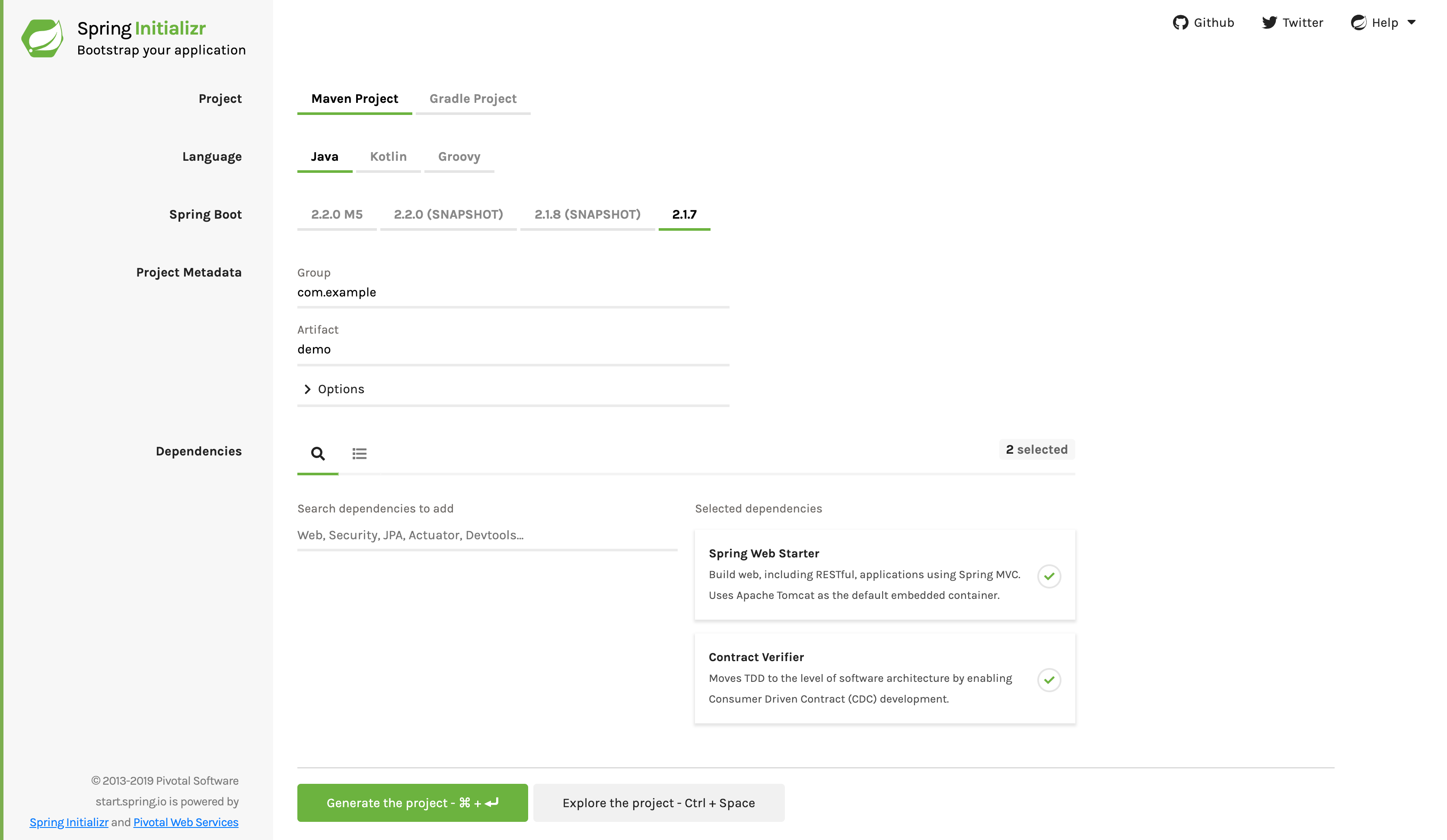
|
现在,您可以使用REST/消息传递协定
以 Groovy DSL 或 YAML 表示到 contracts 目录,该目录由contractsDslDir财产。默认情况下,它是$rootDir/src/test/resources/contracts.
请注意,文件名无关紧要。您可以在此
目录中。
对于 HTTP 存根,协定定义了应为 给定的请求(考虑 HTTP 方法、URL、标头、状态代码等 on) 的 S S以下示例显示了 Groovy 和 YAML 中的 HTTP 存根 Contract:
- 槽的
-
org.springframework.cloud.contract.spec.Contract.make { request { method 'PUT' url '/fraudcheck' body([ "client.id": $(regex('[0-9]{10}')), loanAmount: 99999 ]) headers { contentType('application/json') } } response { status OK() body([ fraudCheckStatus: "FRAUD", "rejection.reason": "Amount too high" ]) headers { contentType('application/json') } } } - YAML
-
request: method: PUT url: /fraudcheck body: "client.id": 1234567890 loanAmount: 99999 headers: Content-Type: application/json matchers: body: - path: $.['client.id'] type: by_regex value: "[0-9]{10}" response: status: 200 body: fraudCheckStatus: "FRAUD" "rejection.reason": "Amount too high" headers: Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8如果需要使用消息传递,您可以定义:
-
输入和输出消息(考虑到它的位置 、邮件正文和标头)。
-
收到消息后应调用的方法。
-
调用时应触发消息的方法。
-
以下示例显示了 Camel 消息传递协定:
- 槽的
-
def contractDsl = Contract.make { name "foo" label 'some_label' input { triggeredBy('bookReturnedTriggered()') } outputMessage { sentTo('activemq:output') body('''{ "bookName" : "foo" }''') headers { header('BOOK-NAME', 'foo') messagingContentType(applicationJson()) } } } - YAML
-
label: some_label input: triggeredBy: bookReturnedTriggered outputMessage: sentTo: activemq:output body: bookName: foo headers: BOOK-NAME: foo contentType: application/json
运行./mvnw clean install自动生成验证应用程序的测试
遵守添加的合同。默认情况下,生成的测试位于org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.tests..
生成的测试可能会有所不同,具体取决于您设置的框架和测试类型 在你的插件中。
在下一个列表中,您可以找到:
-
HTTP Contract 的默认测试模式
MockMvc -
具有
JAXRS测试模式 -
一个
WebTestClient的测试(在使用 反应性的Web-Flux-based applications) 与WEBTESTCLIENT测试模式
| 您只需要其中一个测试框架。MockMvc 是默认值。要使用一个 ,将其库添加到您的 Classpath 中。 |
下面的清单显示了所有框架的示例:
- MOCKMVC
-
@Test public void validate_shouldMarkClientAsFraud() throws Exception { // given: MockMvcRequestSpecification request = given() .header("Content-Type", "application/vnd.fraud.v1+json") .body("{\"client.id\":\"1234567890\",\"loanAmount\":99999}"); // when: ResponseOptions response = given().spec(request) .put("/fraudcheck"); // then: assertThat(response.statusCode()).isEqualTo(200); assertThat(response.header("Content-Type")).matches("application/vnd.fraud.v1.json.*"); // and: DocumentContext parsedJson = JsonPath.parse(response.getBody().asString()); assertThatJson(parsedJson).field("['fraudCheckStatus']").matches("[A-Z]{5}"); assertThatJson(parsedJson).field("['rejection.reason']").isEqualTo("Amount too high"); } - 贾克斯
-
public class FooTest { WebTarget webTarget; @Test public void validate_() throws Exception { // when: Response response = webTarget .path("/users") .queryParam("limit", "10") .queryParam("offset", "20") .queryParam("filter", "email") .queryParam("sort", "name") .queryParam("search", "55") .queryParam("age", "99") .queryParam("name", "Denis.Stepanov") .queryParam("email", "[email protected]") .request() .build("GET") .invoke(); String responseAsString = response.readEntity(String.class); // then: assertThat(response.getStatus()).isEqualTo(200); // and: DocumentContext parsedJson = JsonPath.parse(responseAsString); assertThatJson(parsedJson).field("['property1']").isEqualTo("a"); } } - webtest客户端
-
@Test public void validate_shouldRejectABeerIfTooYoung() throws Exception { // given: WebTestClientRequestSpecification request = given() .header("Content-Type", "application/json") .body("{\"age\":10}"); // when: WebTestClientResponse response = given().spec(request) .post("/check"); // then: assertThat(response.statusCode()).isEqualTo(200); assertThat(response.header("Content-Type")).matches("application/json.*"); // and: DocumentContext parsedJson = JsonPath.parse(response.getBody().asString()); assertThatJson(parsedJson).field("['status']").isEqualTo("NOT_OK"); }
由于合同中描述的功能尚未实现 存在,则测试失败。
要使它们通过,您必须添加处理 HTTP 的正确实现
请求或消息。此外,您必须为自动生成的
tests 添加到项目中。这个类由所有自动生成的测试扩展,并且应该
包含运行它们所需的所有设置必要信息(例如,RestAssuredMockMvc控制器设置或消息传递测试设置)。
以下示例来自pom.xml显示了如何指定 Base Test 类:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<baseClassForTests>com.example.contractTest.BaseTestClass</baseClassForTests> (1)
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>| 1 | 这baseClassForTests元素允许您指定基本测试类。它必须是 child
的configuration元素spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin. |
以下示例显示了一个最小(但功能正常)的基测试类:
package com.example.contractTest;
import org.junit.Before;
import io.restassured.module.mockmvc.RestAssuredMockMvc;
public class BaseTestClass {
@Before
public void setup() {
RestAssuredMockMvc.standaloneSetup(new FraudController());
}
}
This minimal class really is all you need to get your tests to work. It serves as a
starting place to which the automatically generated tests attach.
Now we can move on to the implementation. For that, we first need a data class, which we
then use in our controller. The following listing shows the data class:
package com.example.Test;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class LoanRequest {
@JsonProperty("client.id")
private String clientId;
private Long loanAmount;
public String getClientId() {
return clientId;
}
public void setClientId(String clientId) {
this.clientId = clientId;
}
public Long getLoanAmount() {
return loanAmount;
}
public void setLoanRequestAmount(Long loanAmount) {
this.loanAmount = loanAmount;
}
}
The preceding class provides an object in which we can store the parameters. Because the
client ID in the contract is called client.id, we need to use the
@JsonProperty("client.id") parameter to map it to the clientId field.
Now we can move along to the controller, which the following listing shows:
package com.example.docTest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class FraudController {
@PutMapping(value = "/fraudcheck", consumes="application/json", produces="application/json")
public String check(@RequestBody LoanRequest loanRequest) { (1)
if (loanRequest.getLoanAmount() > 10000) { (2)
return "{fraudCheckStatus: FRAUD, rejection.reason: Amount too high}"; (3)
} else {
return "{fraudCheckStatus: OK, acceptance.reason: Amount OK}"; (4)
}
}
}
1
We map the incoming parameters to a LoanRequest object.
2
We check the requested loan amount to see if it is too much.
3
If it is too much, we return the JSON (created with a simple string here) that the
test expects.
4
If we had a test to catch when the amount is allowable, we could match it to this output.
The FraudController is about as simple as things get. You can do much more, including
logging, validating the client ID, and so on.
Once the implementation and the test base class are in place, the tests pass, and both the
application and the stub artifacts are built and installed in the local Maven repository.
Information about installing the stubs jar to the local repository appears in the logs, as
the following example shows:
[INFO] --- spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin:1.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT:generateStubs (default-generateStubs) @ http-server ---
[INFO] Building jar: /some/path/http-server/target/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-stubs.jar
[INFO]
[INFO] --- maven-jar-plugin:2.6:jar (default-jar) @ http-server ---
[INFO] Building jar: /some/path/http-server/target/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
[INFO]
[INFO] --- spring-boot-maven-plugin:1.5.5.BUILD-SNAPSHOT:repackage (default) @ http-server ---
[INFO]
[INFO] --- maven-install-plugin:2.5.2:install (default-install) @ http-server ---
[INFO] Installing /some/path/http-server/target/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar to /path/to/your/.m2/repository/com/example/http-server/0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
[INFO] Installing /some/path/http-server/pom.xml to /path/to/your/.m2/repository/com/example/http-server/0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.pom
[INFO] Installing /some/path/http-server/target/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-stubs.jar to /path/to/your/.m2/repository/com/example/http-server/0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-stubs.jar
You can now merge the changes and publish both the application and the stub artifacts
in an online repository.
On the Consumer Side
You can use Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner in the integration tests to get a running
WireMock instance or messaging route that simulates the actual service.
To get started, add the dependency to Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner, as follows:
You can get the Producer-side stubs installed in your Maven repository in either of two
ways:
-
By checking out the Producer side repository and adding contracts and generating the
stubs by running the following commands:
$ cd local-http-server-repo
$ ./mvnw clean install -DskipTests
The tests are skipped because the Producer-side contract implementation is not yet
in place, so the automatically-generated contract tests fail.
-
By getting existing producer service stubs from a remote repository. To do so,
pass the stub artifact IDs and artifact repository URL as Spring Cloud Contract Stub
Runner properties, as the following example shows:
Now you can annotate your test class with @AutoConfigureStubRunner. In the annotation,
provide the group-id and artifact-id for Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner to run
the collaborators' stubs for you, as the following example shows:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment=WebEnvironment.NONE)
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:+:stubs:6565"},
stubsMode = StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.LOCAL)
public class LoanApplicationServiceTests {
. . .
}
Use the REMOTE stubsMode when downloading stubs from an online repository and
LOCAL for offline work.
In your integration test, you can receive stubbed versions of HTTP responses or messages
that are expected to be emitted by the collaborator service. You can see entries similar
to the following in the build logs:
2016-07-19 14:22:25.403 INFO 41050 --- [ main] o.s.c.c.stubrunner.AetherStubDownloader : Desired version is + - will try to resolve the latest version
2016-07-19 14:22:25.438 INFO 41050 --- [ main] o.s.c.c.stubrunner.AetherStubDownloader : Resolved version is 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
2016-07-19 14:22:25.439 INFO 41050 --- [ main] o.s.c.c.stubrunner.AetherStubDownloader : Resolving artifact com.example:http-server:jar:stubs:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT using remote repositories []
2016-07-19 14:22:25.451 INFO 41050 --- [ main] o.s.c.c.stubrunner.AetherStubDownloader : Resolved artifact com.example:http-server:jar:stubs:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT to /path/to/your/.m2/repository/com/example/http-server/0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-stubs.jar
2016-07-19 14:22:25.465 INFO 41050 --- [ main] o.s.c.c.stubrunner.AetherStubDownloader : Unpacking stub from JAR [URI: file:/path/to/your/.m2/repository/com/example/http-server/0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/http-server-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-stubs.jar]
2016-07-19 14:22:25.475 INFO 41050 --- [ main] o.s.c.c.stubrunner.AetherStubDownloader : Unpacked file to [/var/folders/0p/xwq47sq106x1_g3dtv6qfm940000gq/T/contracts100276532569594265]
2016-07-19 14:22:27.737 INFO 41050 --- [ main] o.s.c.c.stubrunner.StubRunnerExecutor : All stubs are now running RunningStubs [namesAndPorts={com.example:http-server:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT:stubs=8080}]