|
此版本仍在开发中,尚未被视为稳定版本。对于最新的稳定版本,请使用 Spring Security 6.4.3! |
基本身份验证
本节详细介绍了 Spring Security 如何为基于 servlet 的应用程序提供基本 HTTP 身份验证的支持。
让我们看一下 HTTP 基本身份验证在 Spring Security 中是如何工作的。 首先,我们看到 WWW-Authenticate 标头被发送回未经身份验证的客户端。
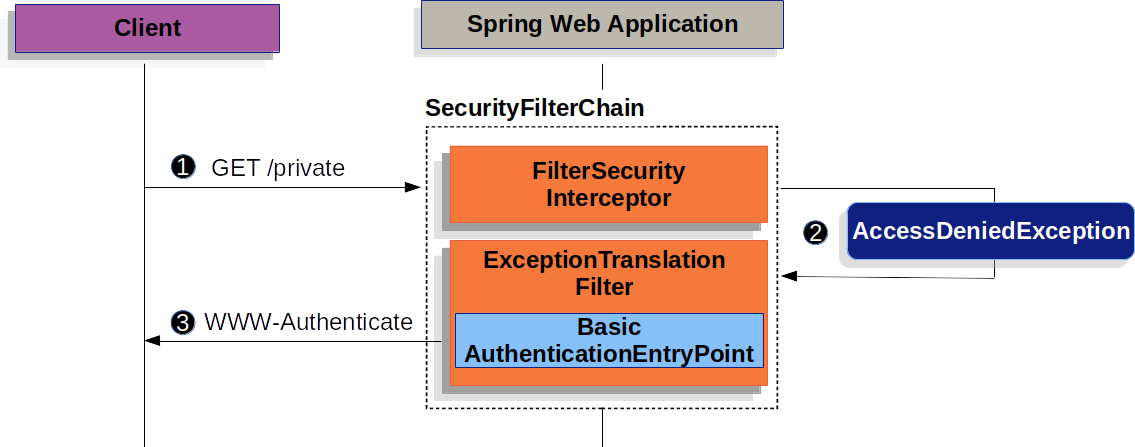
该图建立在我们的SecurityFilterChain图。
![]() 首先,用户向资源发出未经身份验证的请求
首先,用户向资源发出未经身份验证的请求/private它未获得授权。
![]() Spring Security 的
Spring Security 的FilterSecurityInterceptor表示未经身份验证的请求被拒绝,方法是抛出AccessDeniedException.
![]() 由于用户未经过身份验证,因此
由于用户未经过身份验证,因此ExceptionTranslationFilter启动 Start Authentication。
配置的AuthenticationEntryPoint是BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint,它发送 WWW-Authenticate 标头。
这RequestCache通常是NullRequestCache这不会保存请求,因为 Client 端能够重放它最初请求的请求。
当客户端收到 WWW-Authenticate 标头时,它知道它应该使用用户名和密码重试。 以下是正在处理的用户名和密码的流程。
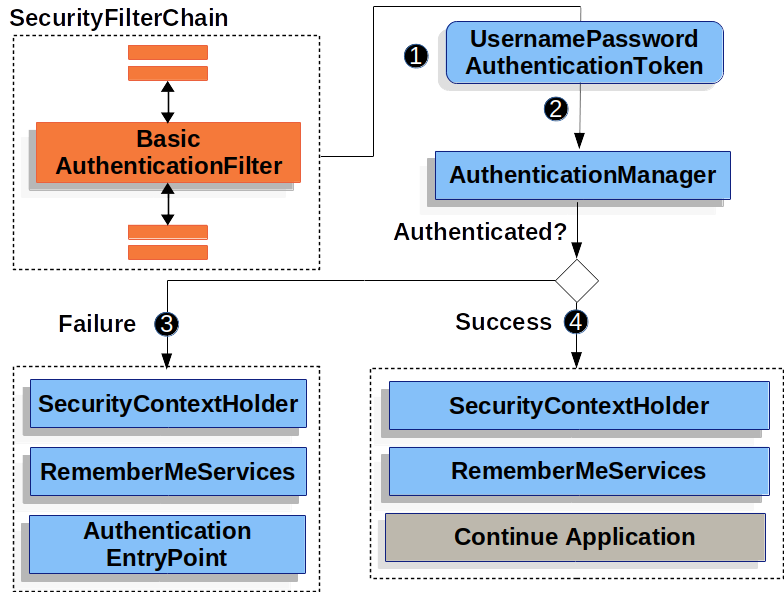
该图建立在我们的SecurityFilterChain图。
![]() 当用户提交其用户名和密码时,
当用户提交其用户名和密码时,BasicAuthenticationFilter创建一个UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken这是一种Authentication通过从HttpServletRequest.
![]() 接下来,
接下来,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken传递到AuthenticationManager进行身份验证。
什么的细节AuthenticationManager看起来取决于用户信息的存储方式。
![]() 如果身份验证失败,则失败
如果身份验证失败,则失败
-
RememberMeServices.loginFail被调用。 如果未配置 Remember me,则为 no-op。 -
AuthenticationEntryPoint以触发 WWW-Authenticate 再次发送。
![]() 如果身份验证成功,则为 Success。
如果身份验证成功,则为 Success。
-
RememberMeServices.loginSuccess被调用。 如果未配置 Remember me,则为 no-op。 -
这
BasicAuthenticationFilter调用FilterChain.doFilter(request,response)以继续执行 Application Logic 的其余部分。
默认情况下,Spring Security 的 HTTP 基本身份验证支持处于启用状态。 但是,一旦提供了任何基于 servlet 的配置,就必须显式提供 HTTP Basic。
可以在下面找到一个最小、明确的配置:
-
Java
-
XML
-
Kotlin
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) {
http
// ...
.httpBasic(withDefaults());
return http.build();
}<http>
<!-- ... -->
<http-basic />
</http>@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
// ...
httpBasic { }
}
return http.build()
}