使用 Spring Cloud Contract
1. 在 Nexus 或 Artifactory 中使用 Stub 进行提供商合同测试
您可以查看开发第一个基于 Spring Cloud Contract 的应用程序链接,以查看在 Nexus 或 Artifactory 流程中使用存根进行提供商 Contract 测试。
您还可以查看研讨会页面,获取有关如何执行此流程的分步说明。
2. 在 Git 中使用存根进行提供商合同测试
在这个流程中,我们执行提供者契约测试(生产者不知道消费者如何使用他们的 API)。存根将上传到单独的存储库(它们不会上传到 Artifactory 或 Nexus)。
2.1. 先决条件
$ tree . └── META-INF └── folder.with.group.id.as.its.name └── folder-with-artifact-id └── folder-with-version ├── contractA.groovy ├── contractB.yml └── contractC.groovy
2.2. 流程
该流程看起来与开发第一个基于 Spring Cloud Contract 的应用程序 中提供的流程完全相同。
但是Stub Storageimplementation 是一个 git 存储库。
您可以阅读有关设置 git 存储库和设置 consumer 和 producer 端的更多信息 在文档的 How To 页面中。
2.3. 消费者设置
为了从 git 存储库而不是 Nexus 或 Artifactory 获取存根,您需要
需要使用git协议的repositoryRoot属性。
以下示例显示了如何设置它:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(
stubsMode = StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE,
repositoryRoot = "git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git",
ids = "com.example:artifact-id:0.0.1")@Rule
public StubRunnerRule rule = new StubRunnerRule()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);@RegisterExtension
public StubRunnerExtension stubRunnerExtension = new StubRunnerExtension()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);2.4. 设置 Producer
为了将存根推送到 git 存储库而不是 Nexus 或 Artifactory,您需要
要使用gitprotocol 的 URL 中。此外,您需要明确告知
用于在构建过程结束时推送存根的插件。以下示例显示了
如何作:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- Base class mappings etc. -->
<!-- We want to pick contracts from a Git repository -->
<contractsRepositoryUrl>git://git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<!-- We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts -->
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</contractDependency>
<!-- The contracts mode can't be classpath -->
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<!-- By default we will not push the stubs back to SCM,
you have to explicitly add it as a goal -->
<goal>pushStubsToScm</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>contracts {
// We want to pick contracts from a Git repository
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:${project.version}"
}
/*
We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts
*/
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "git://git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git"
}
// The mode can't be classpath
contractsMode = "REMOTE"
// Base class mappings etc.
}
/*
In this scenario we want to publish stubs to SCM whenever
the `publish` task is executed
*/
publish.dependsOn("publishStubsToScm")您可以在文档的 How To 页面中阅读有关设置 git 存储库的更多信息。
3. 消费者驱动的合约,生产者端的合约
查看 Consumer Driven 分步指南 Contracts (CDC) 与 Contracts 在 Producer 端查看 Consumer Driven Contracts with Contract on the producer side 流。
4. 具有外部存储库中的合同的消费者驱动合同
在这个流程中,我们执行 Consumer Driven Contract 测试。合同定义包括 存储在单独的存储库中。
有关如何执行此流程的分步说明,请参阅研讨会页面。
4.1. 先决条件
要将消费者驱动的合同与外部存储库中保存的合同一起使用,您需要设置一个 git 存储库,该存储库:
-
包含每个生产者的所有合同定义。
-
可以将 Contract 定义打包到 JAR 中。
-
对于每个合同生成者,包含一个方式(例如
pom.xml) 安装 stub 通过 Spring Cloud Contract Plugin(SCC Plugin)在本地
您还需要设置了 Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner 的使用者代码。 有关此类项目的示例,请参阅此示例。 您还需要设置了 Spring Cloud Contract 的生产者代码以及插件。 有关此类项目的示例,请参阅此示例。 存根存储是 Nexus 或 Artifactory
概括地说,流程如下所示:
-
使用者使用来自单独存储库的合同定义
-
一旦消费者的工作完成,一个带有工作代码的分支就会在消费者身上完成 side 的 PULL MANAGER,并向包含合同定义的单独存储库发出拉取请求。
-
创建者通过 Contract 接管对单独存储库的拉取请求 定义并在本地安装包含所有 Contract 的 JAR。
-
创建者从本地存储的 JAR 生成测试,并写入缺失的 implementation 使测试通过。
-
创建者的工作完成后,对包含该 Contract definitions 被合并。
-
在 CI 工具使用合约定义构建存储库并使用 JAR 合约定义上传到 Nexus 或 Artifactory,生产者可以合并其分支。
-
最后,消费者可以切换到在线工作,从 remote 位置,并且该分支可以合并到 master 中。
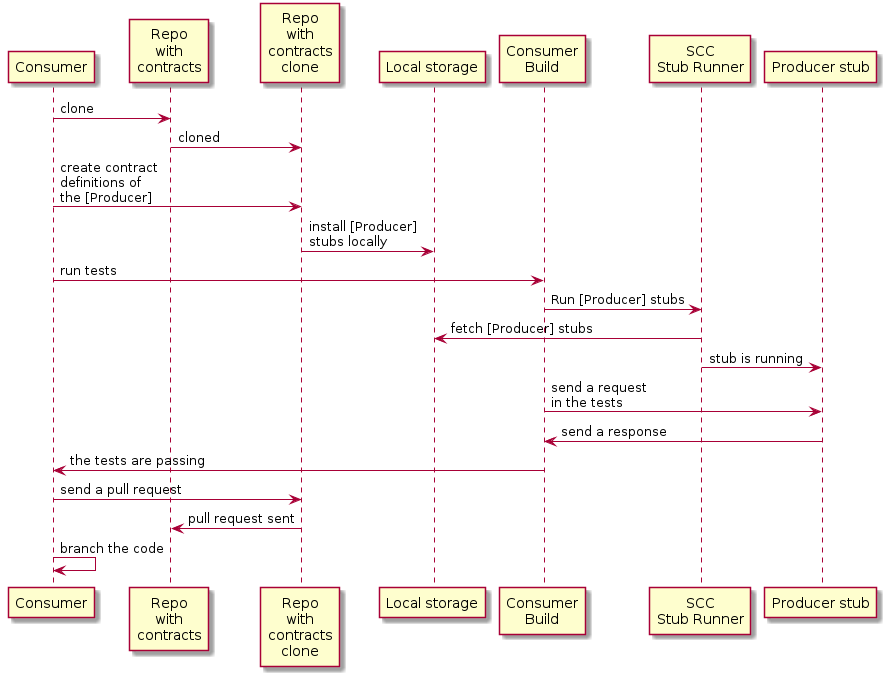
4.2. 消费者流程
消费者:
-
编写一个测试,该测试将向创建者发送请求。
由于没有服务器存在,测试失败。
-
克隆包含合同定义的存储库。
-
将要求设置为文件夹下的合同,并将使用者名称作为生产者的子文件夹。
例如,对于名为
producer和一个名为consumer,合约将存储在src/main/resources/contracts/producer/consumer/) -
定义 Contract 后,将 producer 存根安装到本地存储,如下例所示:
$ cd src/main/resource/contracts/producer $ ./mvnw clean install
-
在使用者测试中设置 Spring Cloud Contract (SCC) Stub Runner,以:
-
从本地存储获取生产者存根。
-
在 stubs-per-consumer 模式下工作(这将启用消费者驱动的 Contract 模式)。
SCC 存根运行程序:
-
获取生产者存根。
-
使用创建器存根运行内存中 HTTP 服务器存根。
-
现在,您的测试与 HTTP 服务器存根通信,并且您的测试通过
-
使用合同定义创建者的新合同创建对存储库的拉取请求
-
对使用者代码进行分支,直到生产者团队合并其代码
-
下面的 UML 图显示了使用者流:
4.3. 生产者流程
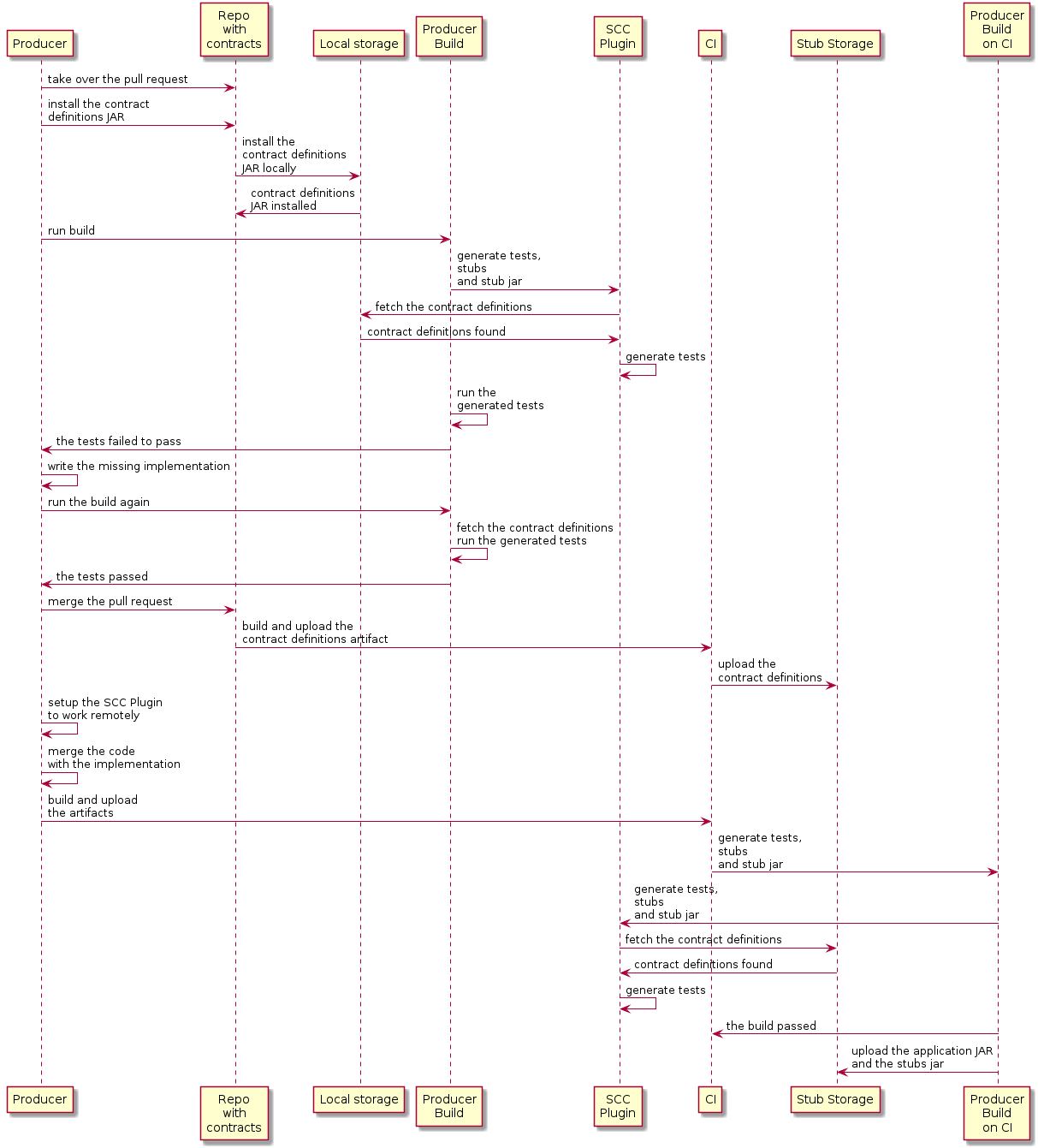
制片人:
-
使用合同定义接管对存储库的拉取请求。你可以的 从命令行,如下所示
$ git checkout -b the_branch_with_pull_request master git pull https://github.com/user_id/project_name.git the_branch_with_pull_request
-
安装合同定义,如下所示
$ ./mvnw clean install
-
设置插件以从 JAR 而不是 JAR 获取协定定义
src/test/resources/contracts如下:Maven 系列<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> <configuration> <!-- We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates --> <contractDependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>beer-contracts</artifactId> </contractDependency> <!-- The JAR with contracts should be taken from Maven local --> <contractsMode>LOCAL</contractsMode> <!-- ... additional configuration --> </configuration> </plugin>Gradlecontracts { // We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates // group id `com.example`, artifact id `beer-contracts`, LATEST version and NO classifier contractDependency { stringNotation = 'com.example:beer-contracts:+:' } // The JAR with contracts should be taken from Maven local contractsMode = "LOCAL" // Additional configuration } -
运行生成以生成测试和存根,如下所示:
Maven 系列./mvnw clean installGradle./gradlew clean build -
写入缺少的实现,以使测试通过。
-
将拉取请求合并到带有合同定义的存储库,如下所示:
$ git commit -am "Finished the implementation to make the contract tests pass" $ git checkout master $ git merge --no-ff the_branch_with_pull_request $ git push origin master
-
CI 系统使用合约定义构建项目,并使用 将合同定义设置为 Nexus 或 Artifactory。
-
切换到远程工作。
-
设置插件,以便不再从本地获取 Contract 定义 存储,但从远程位置存储,如下所示:
Maven 系列<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> <configuration> <!-- We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates --> <contractDependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>beer-contracts</artifactId> </contractDependency> <!-- The JAR with contracts should be taken from a remote location --> <contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode> <!-- ... additional configuration --> </configuration> </plugin>Gradlecontracts { // We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates // group id `com.example`, artifact id `beer-contracts`, LATEST version and NO classifier contractDependency { stringNotation = 'com.example:beer-contracts:+:' } // The JAR with contracts should be taken from a remote location contractsMode = "REMOTE" // Additional configuration } -
将创建者代码与新实现合并。
-
CI 系统:
-
构建项目
-
生成测试、存根和存根 JAR
-
将包含应用程序和存根的工件上传到 Nexus 或 Artifactory。
-
下面的 UML 图显示了生产者进程:
5. 消费者驱动的合约,生产者端的合约,推送到 Git
您可以查看位于生产者端的合同的消费者驱动型合同分步指南 (CDC),以查看在生产者端使用合同的消费者驱动型合同流程。
存根存储实现是一个 git 存储库。我们在 在 Git 中使用存根进行提供商合同测试 部分介绍了它的设置。
您可以在 文档的 How To 页面。
6. 在 Artifactory 中使用非 Spring 应用程序的存根进行提供者合同测试
6.1. 流程
您可以检查开发第一个基于 Spring Cloud Contract 的应用程序,以查看在 Nexus 或 Artifactory 中使用存根进行提供程序 Contract 测试的流程。
6.2. 设置 Consumer
对于使用者端,您可以使用 JUnit 规则。这样,你就不需要启动 Spring 上下文。下面的清单显示了这样的规则(在 JUnit4 和 JUnit 5 中);
@Rule
public StubRunnerRule rule = new StubRunnerRule()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);@Rule
public StubRunnerExtension stubRunnerExtension = new StubRunnerExtension()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);6.3. 设置 Producer
默认情况下,Spring Cloud Contract 插件使用 Rest Assure 的MockMvcsetup 的
生成的测试。由于非 Spring 应用程序不使用MockMvc中,您可以更改testMode自EXPLICIT向绑定在特定端口的应用程序发送真实请求。
在此示例中,我们使用一个名为 Javalin 的框架来启动 非 Spring HTTP 服务器。
假设我们有以下应用程序:
package com.example.demo;
import io.javalin.Javalin;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DemoApplication().run(7000);
}
public Javalin start(int port) {
return Javalin.create().start(port);
}
public Javalin registerGet(Javalin app) {
return app.get("/", ctx -> ctx.result("Hello World"));
}
public Javalin run(int port) {
return registerGet(start(port));
}
}给定该应用程序,我们可以设置插件以使用EXPLICIT模式(即
向真实端口发送请求),如下所示:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<baseClassForTests>com.example.demo.BaseClass</baseClassForTests>
<!-- This will setup the EXPLICIT mode for the tests -->
<testMode>EXPLICIT</testMode>
</configuration>
</plugin>contracts {
// This will setup the EXPLICIT mode for the tests
testMode = "EXPLICIT"
baseClassForTests = "com.example.demo.BaseClass"
}基类可能类似于以下内容:
import io.javalin.Javalin;
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.springframework.util.SocketUtils;
public class BaseClass {
Javalin app;
@Before
public void setup() {
// pick a random port
int port = SocketUtils.findAvailableTcpPort();
// start the application at a random port
this.app = start(port);
// tell Rest Assured where the started application is
RestAssured.baseURI = "http://localhost:" + port;
}
@After
public void close() {
// stop the server after each test
this.app.stop();
}
private Javalin start(int port) {
// reuse the production logic to start a server
return new DemoApplication().run(port);
}
}使用这样的设置:
-
我们已经设置了 Spring Cloud Contract 插件来使用
EXPLICITmode 发送 Real requests 而不是 mock 的。 -
我们定义了一个基类:
-
在每个测试的随机端口上启动 HTTP 服务器。
-
将 Rest Assured 设置为向该端口发送请求。
-
在每次测试后关闭 HTTP 服务器。
-
7. 在非 JVM 环境中使用 Artifactory 中的存根进行提供者合同测试
在此流程中,我们假设:
-
API 创建者和 API 使用者是非 JVM 应用程序。
-
协定定义是用 YAML 编写的。
-
存根存储是 Artifactory 或 Nexus。
-
Spring Cloud Contract Docker (SCC Docker) 和 Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner Docker (SCC Stub Runner Docker) 映像。
您可以在此页面中阅读有关如何将 Spring Cloud Contract 与 Docker 结合使用的更多信息。
在这里,您可以 阅读有关如何在多语言世界中使用 Spring Cloud Contract 的博客文章。
在这里,您可以找到 一个 NodeJS 应用程序示例,该应用程序同时使用 Spring Cloud Contract 作为生产者和 消费者。
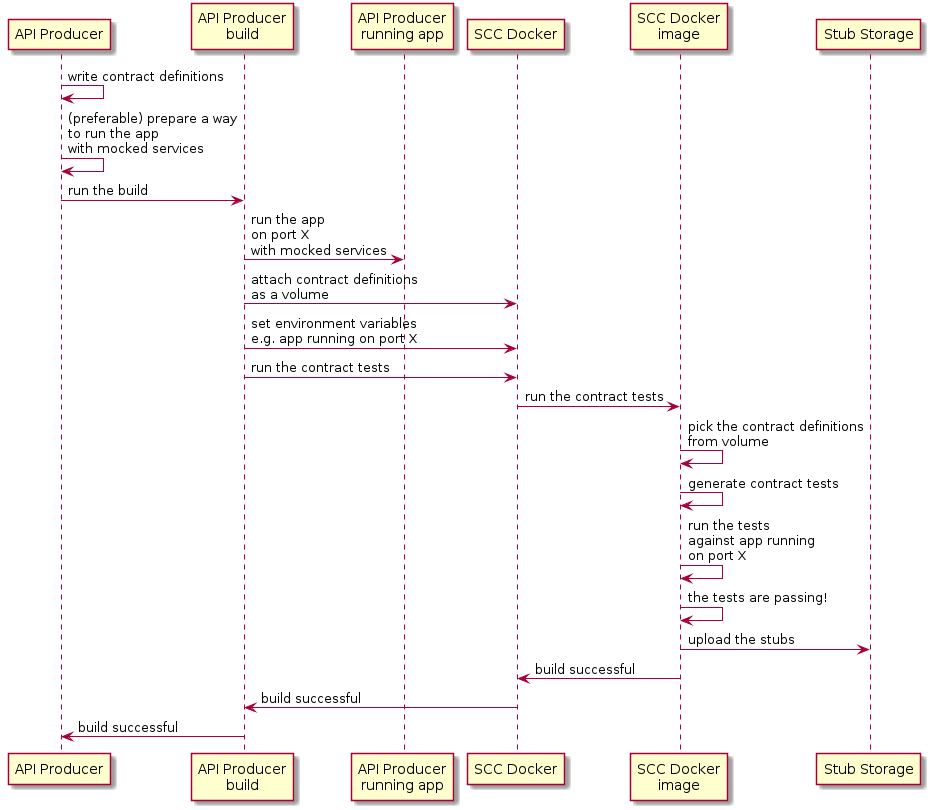
7.1. 生产者流程
在高级别上,生产商:
-
写入协定定义(例如,在 YAML 中)。
-
将生成工具设置为:
-
在给定端口上使用模拟服务启动应用程序。
如果无法进行模拟,您可以设置基础设施并以有状态的方式定义测试。
-
运行 Spring Cloud Contract Docker 镜像,并将正在运行的应用程序的端口作为环境变量传递。
-
SCC Docker 镜像: * 从附加的卷生成测试。 * 针对正在运行的应用程序运行测试。
测试完成后,存根将上传到存根存储站点(例如 Artifactory 或 Git)。
以下 UML 图显示了生产者流程:
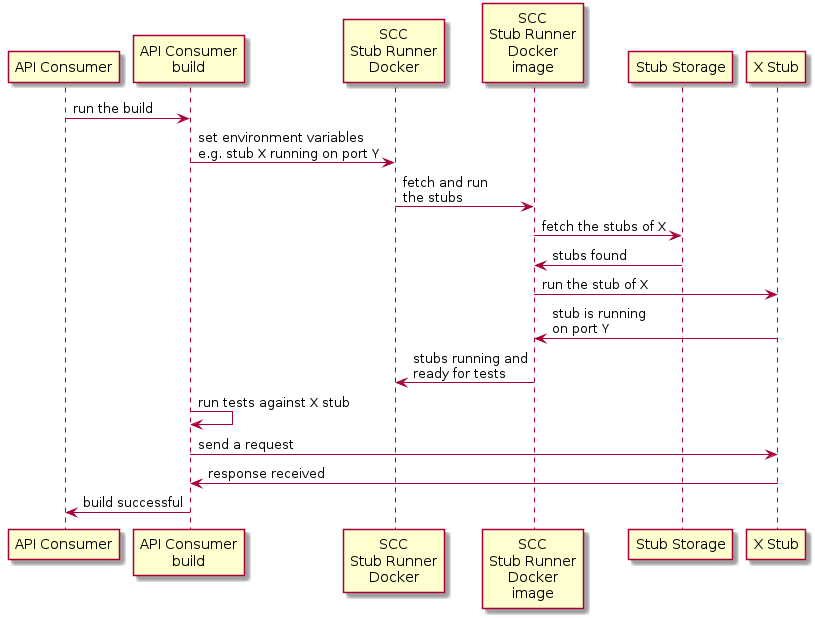
7.2. 消费者流程
在高级别上,消费者:
-
将生成工具设置为:
-
启动 Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner Docker 镜像并启动存根。
环境变量配置:
-
要获取的存根。
-
存储库的位置。
请注意:
-
要使用本地存储,您还可以将其附加为卷。
-
需要公开运行存根的端口。
-
-
针对正在运行的存根运行应用程序测试。
下面的 UML 图显示了使用者流:
8. 在 Nexus 或 Artifactory 中使用 REST 文档和存根进行提供商合同测试
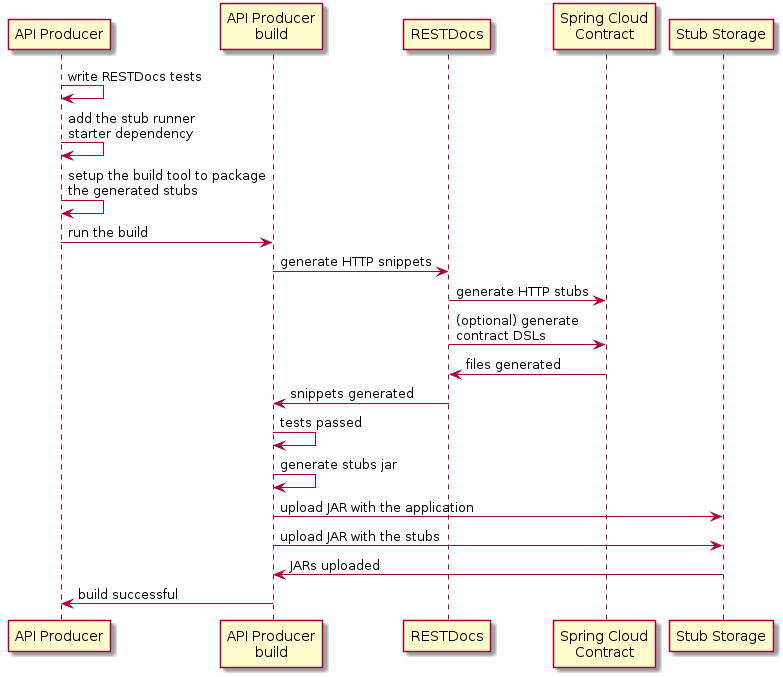
在此流程中,我们不使用 Spring Cloud Contract 插件来生成测试和存根。我们编写 Spring RESTDoc,并从中自动生成存根。最后,我们设置构建来打包存根并将它们上传到存根存储站点 — 在我们的例子中,是 Nexus 或 Artifactory。
有关如何使用此流程的分步说明,请参阅研讨会页面。
8.1. 生产者流程
作为生产商,我们:
-
我们编写 API 的 RESTDocs 测试。
-
我们将 Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner starter 添加到我们的构建中(
spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner),如下所示maven<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>Gradledependencies { testImplementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner' } dependencyManagement { imports { mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}" } } -
我们设置构建工具来打包我们的存根,如下所示:
maven<!-- pom.xml --> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId> <executions> <execution> <id>stub</id> <phase>prepare-package</phase> <goals> <goal>single</goal> </goals> <inherited>false</inherited> <configuration> <attach>true</attach> <descriptors> ${basedir}/src/assembly/stub.xml </descriptors> </configuration> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> <!-- src/assembly/stub.xml --> <assembly xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/assembly-1.1.3.xsd"> <id>stubs</id> <formats> <format>jar</format> </formats> <includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory> <fileSets> <fileSet> <directory>${project.build.directory}/generated-snippets/stubs</directory> <outputDirectory>META-INF/${project.groupId}/${project.artifactId}/${project.version}/mappings</outputDirectory> <includes> <include>**/*</include> </includes> </fileSet> </fileSets> </assembly>Gradletask stubsJar(type: Jar) { classifier = "stubs" into("META-INF/${project.group}/${project.name}/${project.version}/mappings") { include('**/*.*') from("${project.buildDir}/generated-snippets/stubs") } } // we need the tests to pass to build the stub jar stubsJar.dependsOn(test) bootJar.dependsOn(stubsJar)
现在,当我们运行测试时,存根会自动发布和打包。
以下 UML 图显示了生产者流程:
8.2. 消费者流程
由于使用者流不受用于生成存根的工具的影响,因此您可以检查开发第一个基于 Spring Cloud Contract 的应用程序,以查看使用 Nexus 或 Artifactor 中的存根进行提供者 Contract 测试的使用者端的流程。
9. 接下来要读什么
现在,您应该了解如何使用 Spring Cloud Contract 以及 应该紧随其后。您现在可以继续了解特定的 Spring Cloud Contract 功能,或者您可以 跳到前面并阅读 Spring Cloud Contract 的高级功能。