“作方法”指南
1. 为什么使用 Spring Cloud Contract?
Spring Cloud Contract 在多语言环境中运行良好。这个项目有很多 非常有趣的功能。其中相当多的功能肯定会使 Spring Cloud Contract Verifier 在消费者驱动合约市场上脱颖而出 (CDC) 工具。最有趣的功能包括:
-
能够使用消息传递进行 CDC。
-
清晰易用的静态类型 DSL。
-
能够将当前 JSON 文件复制粘贴到合同中,并且仅编辑其元素。
-
从定义的 Contract 自动生成测试。
-
Stub Runner 功能:存根在运行时自动从 Nexus/Artifactory 下载。
-
Spring Cloud 集成:集成测试不需要发现服务。
-
Spring Cloud Contract 与 Pact 集成,并提供简单的钩子来扩展其功能。
-
能够通过Docker添加对任何语言和框架的支持。
2. 如何用 Groovy 以外的语言编写合约?
您可以在 YAML 中编写 Contract。有关更多信息,请参阅此部分。
我们正在努力允许更多方式来描述合约。您可以查看 github-issues 了解更多信息。
3. 如何为合约提供动态值?
与 stub 相关的最大挑战之一是它们的可重用性。只有它们能够得到广泛使用,它们才能达到其目的。 请求和响应元素的硬编码值(例如日期和 ID)通常会使这变得困难。 请考虑以下 JSON 请求:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 20:10:15",
"id" : "9febab1c-6f36-4a0b-88d6-3b6a6d81cd4a",
"body" : "foo"
}现在考虑以下 JSON 响应:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 21:10:15",
"id" : "c4231e1f-3ca9-48d3-b7e7-567d55f0d051",
"body" : "bar"
}想象一下,设置time字段(假设此内容由
database) 通过更改系统中的 clock 或通过提供数据提供程序的存根实现。同样是相关的
添加到名为id.您可以创建 UUID 生成器的存根实现,但这样做几乎没有意义。
因此,作为使用者,您希望发送与任何形式的时间或任何 UUID 匹配的请求。这样,您的系统
像往常一样工作,无需您存根任何内容即可生成数据。假设,在上述情况下
JSON 中,最重要的部分是body田。您可以专注于此并为其他字段提供匹配。换句话说,
您希望存根的工作方式如下:
{
"time" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES TIME",
"id" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES UUID",
"body" : "foo"
}就响应而言,作为消费者,您需要一个可以作的具体价值。 因此,以下 JSON 有效:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 21:10:15",
"id" : "c4231e1f-3ca9-48d3-b7e7-567d55f0d051",
"body" : "bar"
}在前面的部分中,我们从 Contract 生成了测试。因此,从生产商的角度来看,情况看起来 大不相同。我们解析提供的 Contract,并在测试中向你的 endpoints 发送一个真实的请求。 因此,对于请求的 producer 的情况,我们不能进行任何形式的匹配。我们需要具体的值,其中 producer 的后端可以工作。因此,以下 JSON 将有效:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 20:10:15",
"id" : "9febab1c-6f36-4a0b-88d6-3b6a6d81cd4a",
"body" : "foo"
}另一方面,从合同有效性的角度来看,回应不一定必须
包含 的具体值time或id.假设您在生产者端生成这些 API。同样,您
必须进行大量 stub 以确保始终返回相同的值。这就是为什么,从生产者的角度来看
您可能需要以下响应:
{
"time" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES TIME",
"id" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES UUID",
"body" : "bar"
}那么,您如何为消费者提供匹配器,为生产者提供具体值(在其他时间则相反)? Spring Cloud Contract 允许您提供动态值。这意味着两者可能不同 沟通的双方。
您可以在 Contract DSL 部分阅读更多相关信息。
| 阅读与 JSON 相关的 Groovy 文档以了解如何 正确构建请求和响应正文。 |
4. 如何进行 Stubs 版本控制?
本节介绍存根的版本,您可以通过多种不同的方式处理这些版本:
4.1. API 版本控制
版本控制的真正含义是什么?如果参考 API 版本,则有 不同的方法:
-
使用超媒体链接,并且不要以任何方式对您的 API 进行版本控制
-
通过标头和 URL 传递版本
我们不试图回答哪种方法更好的问题。你应该选择任何东西 满足您的需求,并让您产生业务价值。
假设您确实对 API 进行了版本控制。在这种情况下,您应该提供尽可能多的合同,以及您支持的版本。 您可以为每个版本创建一个子文件夹,也可以将其附加到合同名称 - 任何最适合您的方式。
4.2. JAR版本控制
如果版本控制是指包含存根的 JAR 版本,那么基本上有两种主要方法。
假设您执行持续交付和部署,这意味着您生成了新版本的 jar 并且 jar 可以随时投入生产。例如,您的 jar 版本 如下所示(因为它是在 2016 年 10 月 20 日 20:15:21 构建的):
1.0.0.20161020-201521-RELEASE在这种情况下,您生成的存根 jar 应如下所示:
1.0.0.20161020-201521-RELEASE-stubs.jar在这种情况下,您应该在application.yml或@AutoConfigureStubRunner什么时候
引用存根,提供存根的最新版本。您可以通过传递 sign 来做到这一点。下面的示例演示如何执行此作:+
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:+:stubs:8080"})但是,如果版本控制是固定的(例如,1.0.4.RELEASE或2.1.1),您必须设置 jar 的具体值
版本。以下示例显示了如何为版本 2.1.1 执行此作:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:2.1.1:stubs:8080"})4.3. 开发或生产存根
您可以作分类器以针对当前开发版本运行测试
其他服务的存根或部署到生产环境的服务。如果您更改
您的构建使用prod-stubs分类器一旦你进入生产环境
部署中,您可以在一种情况下使用开发存根运行测试,另一种情况下使用生产存根运行测试。
以下示例适用于使用存根的开发版本的测试:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:+:stubs:8080"})以下示例适用于使用存根的生产版本的测试:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:+:prod-stubs:8080"})您还可以在部署管道的属性中传递这些值。
5. 如何将公共仓库与合约一起使用,而不是将它们存储在 Producer 中?
另一种存储合同的方法,而不是将它们与生产者一起保存 他们在一个共同的地方。这种情况可能与安全问题有关(其中 使用者无法克隆创建者的代码)。此外,如果您将 Contract 保存在一个地方, 然后,作为生产者,您知道您有多少个使用者以及您可能会打破哪个使用者 替换为您的本地更改。
5.1. 仓库结构
假设我们有一个坐标为com.example:server和三个
消费者:client1,client2和client3.然后,在具有 common 的
合约,您可以进行以下设置(您可以在此处查看)。
下面的清单显示了这样的结构:
├── com
│ └── example
│ └── server
│ ├── client1
│ │ └── expectation.groovy
│ ├── client2
│ │ └── expectation.groovy
│ ├── client3
│ │ └── expectation.groovy
│ └── pom.xml
├── mvnw
├── mvnw.cmd
├── pom.xml
└── src
└── assembly
└── contracts.xml正如您在斜杠分隔的groupid/artifact id文件夹 (com/example/server)
三个消费者的期望 (client1,client2和client3).期望是标准的 Groovy DSL
Contract 文件,如本文档中所述。此存储库必须生成一个 JAR 文件,该文件将
一对一到存储库的内容。
以下示例显示了pom.xml在server文件夹:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>server</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
<name>Server Stubs</name>
<description>POM used to install locally stubs for consumer side</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.10.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud-contract.version>2.2.8.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</spring-cloud-contract.version>
<spring-cloud-release.version>Hoxton.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</spring-cloud-release.version>
<excludeBuildFolders>true</excludeBuildFolders>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-release.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- By default it would search under src/test/resources/ -->
<contractsDirectory>${project.basedir}</contractsDirectory>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<name>Spring Releases</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/release</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<name>Spring Releases</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/release</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>除了 Spring Cloud Contract Maven 插件之外,没有其他依赖项。
这些 pom 文件是使用者端运行所必需的mvn clean install -DskipTests本地安装
Producer 项目的存根。
这pom.xml在根文件夹中,可能如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example.standalone</groupId>
<artifactId>contracts</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
<name>Contracts</name>
<description>Contains all the Spring Cloud Contracts, well, contracts. JAR used by the
producers to generate tests and stubs
</description>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>contracts</id>
<phase>prepare-package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<attach>true</attach>
<descriptor>${basedir}/src/assembly/contracts.xml</descriptor>
<!-- If you want an explicit classifier remove the following line -->
<appendAssemblyId>false</appendAssemblyId>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>它使用汇编插件来构建包含所有协定的 JAR。以下示例 显示了这样的设置:
<assembly xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/assembly-1.1.3.xsd">
<id>project</id>
<formats>
<format>jar</format>
</formats>
<includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory>
<fileSets>
<fileSet>
<directory>${project.basedir}</directory>
<outputDirectory>/</outputDirectory>
<useDefaultExcludes>true</useDefaultExcludes>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/${project.build.directory}/**</exclude>
<exclude>mvnw</exclude>
<exclude>mvnw.cmd</exclude>
<exclude>.mvn/**</exclude>
<exclude>src/**</exclude>
</excludes>
</fileSet>
</fileSets>
</assembly>5.2. 工作流程
该工作流假定 Spring Cloud Contract 同时在使用者和 producer 端。在公共存储库中还有适当的插件设置,其中 合同。CI 作业是为公共存储库设置的,以构建所有 合同并将其上传到 Nexus/Artifactory。下图显示了此 UML 工作流程:
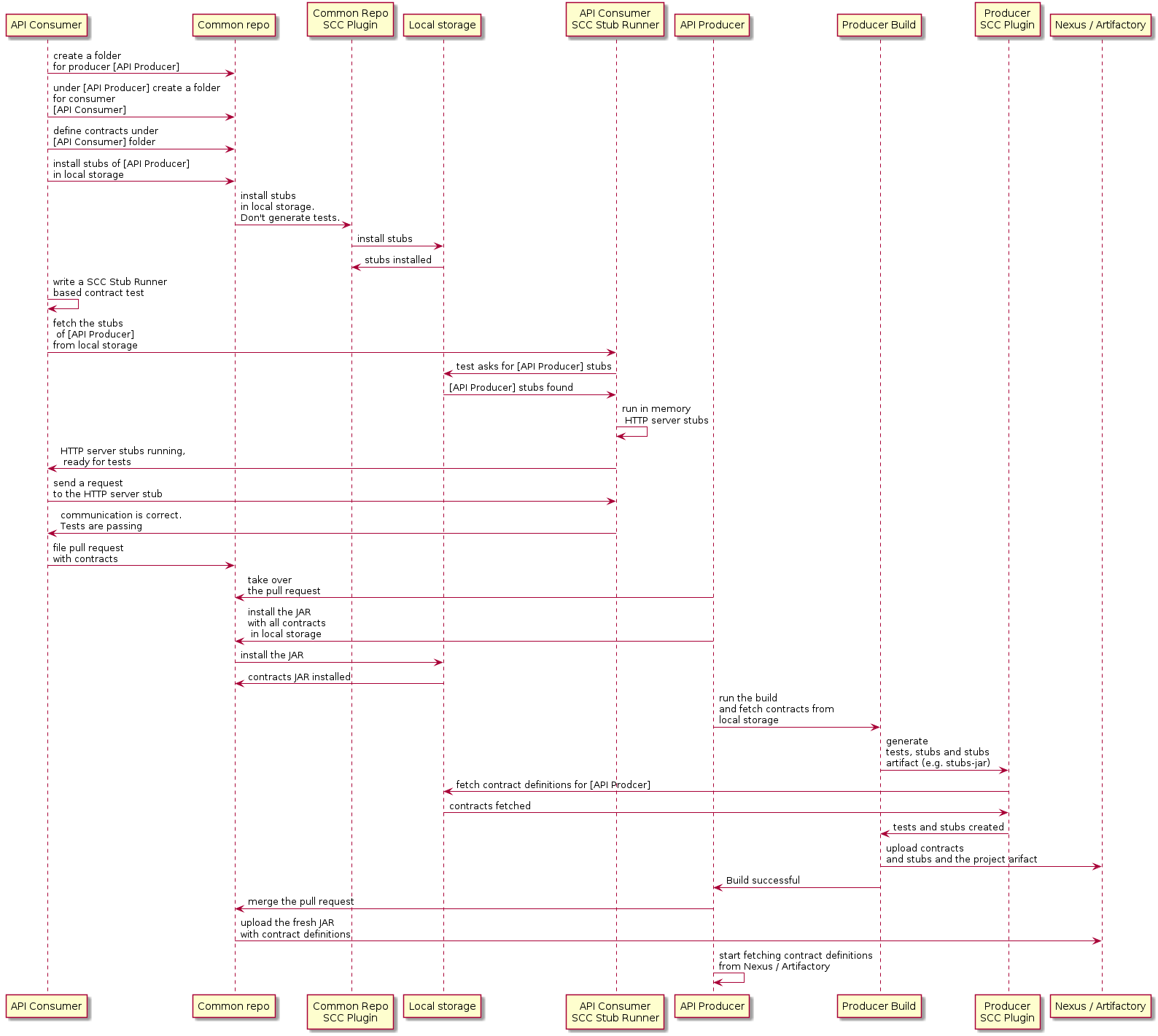
5.3. 消费者
当消费者想要离线处理 Contract 而不是克隆 producer 时
code 中,使用者团队会克隆公共存储库,然后转到所需的创建者的
文件夹(例如com/example/server) 并运行mvn clean install -DskipTests自
在本地安装从 Contract 转换的 stub。
| 您需要在本地安装 Maven |
5.4. 生产者
作为生产者,您可以更改 Spring Cloud Contract Verifier 以提供 URL 和 包含 Contract 的 JAR 的依赖项,如下所示:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
<contractsRepositoryUrl>
https://link/to/your/nexus/or/artifactory/or/sth
</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<contractDependency>
<groupId>com.example.standalone</groupId>
<artifactId>contracts</artifactId>
</contractDependency>
</configuration>
</plugin>通过此设置,groupid 为com.example.standalone和 artifactidcontracts下载自link/to/your/nexus/or/artifactory/or/sth.是的
然后解压缩到本地临时文件夹中,并且com/example/server被选为用于生成测试和存根的文件。由于
根据这个约定,生产者团队可以知道哪些消费者团队会在什么时候被破坏
进行了一些不兼容的更改。
流的其余部分看起来相同。
5.5. 如何定义每个主题而不是每个生产者的消息收发合同?
为避免公共存储库中的消息传递协定重复,当几个生产者将消息写入一个主题时, 我们可以创建一个结构,其中 REST 合同放置在每个生产者和消息传递的文件夹中 合同放置在每个主题的文件夹中。
5.5.1. 对于 Maven 项目
为了能够在生产者端工作,我们应该为
按我们感兴趣的消息主题筛选常见的存储库 JAR 文件。这includedFilesMaven Spring Cloud Contract 插件的属性
让我们这样做。也contractsPath需要指定,因为默认路径为
通用存储库groupid/artifactid.以下示例显示了一个 Maven
Spring Cloud Contract 插件:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<configuration>
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
<contractsRepositoryUrl>https://link/to/your/nexus/or/artifactory/or/sth</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<contractDependency>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>common-repo-with-contracts</artifactId>
<version>+</version>
</contractDependency>
<contractsPath>/</contractsPath>
<baseClassMappings>
<baseClassMapping>
<contractPackageRegex>.*messaging.*</contractPackageRegex>
<baseClassFQN>com.example.services.MessagingBase</baseClassFQN>
</baseClassMapping>
<baseClassMapping>
<contractPackageRegex>.*rest.*</contractPackageRegex>
<baseClassFQN>com.example.services.TestBase</baseClassFQN>
</baseClassMapping>
</baseClassMappings>
<includedFiles>
<includedFile>**/${project.artifactId}/**</includedFile>
<includedFile>**/${first-topic}/**</includedFile>
<includedFile>**/${second-topic}/**</includedFile>
</includedFiles>
</configuration>
</plugin>| 上述 Maven 插件中的许多值都可以更改。我们将其包括 说明目的,而不是试图提供一个 “典型 ”的例子。 |
5.5.2. 对于 Gradle 项目
要使用 Gradle 项目,请执行以下作:
-
为常见的存储库依赖项添加自定义配置,如下所示:
ext { contractsGroupId = "com.example" contractsArtifactId = "common-repo" contractsVersion = "1.2.3" } configurations { contracts { transitive = false } } -
将 common repository 依赖项添加到您的 Classpath 中,如下所示:
dependencies { contracts "${contractsGroupId}:${contractsArtifactId}:${contractsVersion}" testCompile "${contractsGroupId}:${contractsArtifactId}:${contractsVersion}" } -
将依赖项下载到相应的文件夹,如下所示:
task getContracts(type: Copy) { from configurations.contracts into new File(project.buildDir, "downloadedContracts") } -
解压缩 JAR,如下所示:
task unzipContracts(type: Copy) { def zipFile = new File(project.buildDir, "downloadedContracts/${contractsArtifactId}-${contractsVersion}.jar") def outputDir = file("${buildDir}/unpackedContracts") from zipTree(zipFile) into outputDir } -
清理未使用的合约,如下所示:
task deleteUnwantedContracts(type: Delete) { delete fileTree(dir: "${buildDir}/unpackedContracts", include: "**/*", excludes: [ "**/${project.name}/**"", "**/${first-topic}/**", "**/${second-topic}/**"]) } -
创建任务依赖关系,如下所示:
unzipContracts.dependsOn("getContracts") deleteUnwantedContracts.dependsOn("unzipContracts") build.dependsOn("deleteUnwantedContracts") -
通过指定包含 Contract 的目录来配置插件,方法是将 这
contractsDslDir属性,如下所示:contracts { contractsDslDir = new File("${buildDir}/unpackedContracts") }
6. 如何使用 Git 作为合约和存根的存储?
在多语言世界中,有些语言不使用二进制存储,如 Artifactory 或 Nexus 可以。从 Spring Cloud Contract 版本 2.0.0 开始,我们提供 在 SCM (Source Control Management) 存储库中存储合同和存根的机制。目前, 唯一支持的 SCM 是 Git。
存储库必须具有以下设置 (您可以从此处查看):
.
└── META-INF
└── com.example
└── beer-api-producer-git
└── 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
├── contracts
│ └── beer-api-consumer
│ ├── messaging
│ │ ├── shouldSendAcceptedVerification.groovy
│ │ └── shouldSendRejectedVerification.groovy
│ └── rest
│ ├── shouldGrantABeerIfOldEnough.groovy
│ └── shouldRejectABeerIfTooYoung.groovy
└── mappings
└── beer-api-consumer
└── rest
├── shouldGrantABeerIfOldEnough.json
└── shouldRejectABeerIfTooYoung.json在META-INF文件夹:
-
我们按以下方式对应用程序进行分组
groupId(例如com.example). -
每个应用程序都由其
artifactId(例如,beer-api-producer-git). -
接下来,每个应用程序都按其版本(例如
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT).开始 从 Spring Cloud Contract 版本2.1.0中,您可以指定版本,如下所示 (假设您的版本遵循语义版本控制):-
+或latest:要查找存根的最新版本(假设快照 始终是给定修订号的最新工件)。这意味着:-
如果你有
1.0.0.RELEASE,2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT和2.0.0.RELEASE,我们假设 最新的是2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT. -
如果你有
1.0.0.RELEASE和2.0.0.RELEASE,我们假设 latest 为2.0.0.RELEASE. -
如果您有一个名为
latest或者,我们将选择该文件夹。+
-
-
release:查找存根的最新版本。这意味着:-
如果你有
1.0.0.RELEASE,2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT和2.0.0.RELEASE我们假设 最新的是2.0.0.RELEASE. -
如果您有一个名为
release,我们选择该文件夹。
-
-
最后,有两个文件夹:
-
contracts:好的做法是存储每个 consumer 中具有 consumer 名称(例如beer-api-consumer).这样,您 可以使用stubs-per-consumer特征。进一步的目录结构是任意的。 -
mappings:Maven 或 Gradle Spring Cloud Contract 插件推送 此文件夹中的存根服务器映射。在使用者端,Stub Runner 会扫描此文件夹 以启动具有存根定义的存根服务器。文件夹结构是一个副本 在contracts子文件夹。
6.1. 协议约定
要控制合约来源的类型和位置(无论 binary storage 或 SCM 存储库),您可以在 存储库。Spring Cloud Contract 迭代已注册的协议解析器 并尝试获取 Contract (通过使用插件) 或 stub (从 Stub Runner)。
对于 SCM 功能,目前我们支持 Git 存储库。要使用它,
在需要放置存储库 URL 的属性中,您必须为存储库 URL 添加前缀
连接 URL 与git://.下面的清单显示了一些示例:
git://file:///foo/bar
git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git
git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git6.2. 生产者
对于生产者,要使用 SCM(源代码控制管理)方法,我们可以重用
我们用于外部合约的机制相同。我们路由 Spring Cloud Contract
使用以
这git://协议。
您必须手动添加pushStubsToScmgoal 或 execute (bind)pushStubsToScmtask 中
Gradle 的 Gradle 中。我们不会将存根推送到origin你的 git
存储 库。 |
以下清单包括 Maven 和 Gradle 构建文件的相关部分:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- Base class mappings etc. -->
<!-- We want to pick contracts from a Git repository -->
<contractsRepositoryUrl>git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<!-- We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts -->
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</contractDependency>
<!-- The contracts mode can't be classpath -->
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<!-- By default we will not push the stubs back to SCM,
you have to explicitly add it as a goal -->
<goal>pushStubsToScm</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>contracts {
// We want to pick contracts from a Git repository
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:${project.version}"
}
/*
We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts
*/
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git"
}
// The mode can't be classpath
contractsMode = "REMOTE"
// Base class mappings etc.
}
/*
In this scenario we want to publish stubs to SCM whenever
the `publish` task is executed
*/
publish.dependsOn("publishStubsToScm")还可以进一步自定义publishStubsToScmgradle 任务。在以下示例中,
该任务经过自定义,可从本地 Git 存储库中选择合同:
publishStubsToScm {
// We want to modify the default set up of the plugin when publish stubs to scm is called
// We want to pick contracts from a Git repository
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:${project.version}"
}
/*
We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts
*/
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "git://file://${new File(project.rootDir, "../target")}/contract_empty_git/"
}
// We set the contracts mode to `LOCAL`
contractsMode = "LOCAL"
}- 重要
-
起始
2.3.0.RELEASE这customize{}之前用于publishStubsToScm自定义不再可用。应直接应用设置 在publishStubsToScmclose 的 SET 方法。
使用这样的设置:
-
将 git 项目克隆到临时目录
-
SCM 存根下载器转到
META-INF/groupId/artifactId/version/contracts文件夹 以查找合同。例如,对于com.example:foo:1.0.0,则路径将为META-INF/com.example/foo/1.0.0/contracts. -
测试是从 Contract 生成的。
-
存根是从 Contract 创建的。
-
测试通过后,存根将提交到克隆的存储库中。
-
最后,将推送发送到该存储库的
origin.
6.3. 本地存储 Contract 的 producer
使用 SCM 作为存根和 Contract 目标的另一种选择是将 与生产者在本地签订合同,并且仅将合同和存根推送到 SCM。 下面的清单显示了使用 Maven 和 Gradle 实现此目的所需的设置:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<!-- In the default configuration, we want to use the contracts stored locally -->
<configuration>
<baseClassMappings>
<baseClassMapping>
<contractPackageRegex>.*messaging.*</contractPackageRegex>
<baseClassFQN>com.example.BeerMessagingBase</baseClassFQN>
</baseClassMapping>
<baseClassMapping>
<contractPackageRegex>.*rest.*</contractPackageRegex>
<baseClassFQN>com.example.BeerRestBase</baseClassFQN>
</baseClassMapping>
</baseClassMappings>
<basePackageForTests>com.example</basePackageForTests>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<!-- By default we will not push the stubs back to SCM,
you have to explicitly add it as a goal -->
<goal>pushStubsToScm</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<!-- We want to pick contracts from a Git repository -->
<contractsRepositoryUrl>git://file://${env.ROOT}/target/contract_empty_git/
</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<!-- Example of URL via git protocol -->
<!--<contractsRepositoryUrl>git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-samples.git</contractsRepositoryUrl>-->
<!-- Example of URL via http protocol -->
<!--<contractsRepositoryUrl>git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-samples.git</contractsRepositoryUrl>-->
<!-- We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts -->
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</contractDependency>
<!-- The mode can't be classpath -->
<contractsMode>LOCAL</contractsMode>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>contracts {
// Base package for generated tests
basePackageForTests = "com.example"
baseClassMappings {
baseClassMapping(".*messaging.*", "com.example.BeerMessagingBase")
baseClassMapping(".*rest.*", "com.example.BeerRestBase")
}
/*
In this scenario we want to publish stubs to SCM whenever
the `publish` task is executed
*/
publishStubsToScm {
// We want to modify the default set up of the plugin when publish stubs to scm is called
// We want to pick contracts from a Git repository
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:${project.version}"
}
/*
We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts
*/
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "git://file://${new File(project.rootDir, "../target")}/contract_empty_git/"
}
// The mode can't be classpath
contractsMode = "LOCAL"
}
}
publish.dependsOn("publishStubsToScm")
publishToMavenLocal.dependsOn("publishStubsToScm")使用这样的设置:
-
默认合同
src/test/resources/contracts目录。 -
测试是从 Contract 生成的。
-
存根是从 Contract 创建的。
-
测试通过后:
-
git 项目被克隆到一个临时目录。
-
存根和合同将在克隆的存储库中提交。
-
-
最后,将推送到该存储库的
origin.
6.4. 将与 Producer 的 Contract 和存根保存在外部存储库中
您还可以将合同保留在创建者存储库中,但将存根保留在外部 git 存储库中。 当您想使用基本消费者-生产者协作流但不能使用时,这最有用 使用构件存储库存储存根。
为此,请使用通常的 producer 设置,然后添加pushStubsToScm目标和设置contractsRepositoryUrl添加到要保留存根的存储库中。
6.5. 消费者
在消费者端,当传递repositoryRoot参数
要么来自@AutoConfigureStubRunnerannotation、
JUnit 规则、JUnit 5 扩展或属性,您可以传递
SCM 存储库,前缀为git://协议。以下示例显示了如何执行此作:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(
stubsMode="REMOTE",
repositoryRoot="git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git",
ids="com.example:bookstore:0.0.1.RELEASE"
)使用这样的设置:
-
git 项目被克隆到一个临时目录。
-
SCM 存根下载器转到 thje
META-INF/groupId/artifactId/version/文件夹 查找存根定义和协定。例如,对于com.example:foo:1.0.0,则路径将为META-INF/com.example/foo/1.0.0/. -
Stub 服务器启动并馈送 Mapping。
-
消息收发定义在消息收发测试中读取和使用。
7. 如何使用 Pact Broker?
使用 Pact 时,您可以使用 Pact Broker 存储和共享 Pact 定义。从 Spring Cloud Contract 开始 2.0.0 中,您可以从 Pact Broker 获取 Pact 文件以生成 测试和存根。
| Pact 遵循消费者契约约定。这意味着 使用者首先创建 Pact 定义,然后 与 Producer 共享文件。这些期望是产生的 从 Consumer 的代码中,如果期望 未得到满足。 |
7.1. 如何使用 Pact
Spring Cloud Contract 包括对 Pact 表示的支持
Contract 直到版本 4。您可以使用 Pact 文件,而不是使用 DSL。在本节中,我们将
演示如何为项目添加 Pact 支持。但请注意,并非所有功能都受支持。
从版本 3 开始,你可以为同一元素组合多个匹配器;
你可以对 body、headers、request 和 path 使用 matchers;并且您可以使用值生成器。
Spring Cloud Contract 目前仅支持使用AND规则逻辑。
接下来,在转换过程中会跳过 request 和 path matcher。
当使用具有给定格式的日期、时间或日期时间值生成器时,
跳过给定的格式,并使用 ISO 格式。
7.2. 契约转换器
为了正确支持 Spring Cloud Contract 的消息传递方式 使用 Pact,您必须提供一些额外的元数据条目。
要定义消息发送到的目标,您必须
设置metaData条目,其中sentTokey 等于目标
要发送的消息(例如"metaData": { "sentTo": "activemq:output" }).
7.3. 契约合约
Spring Cloud Contract 可以读取 Pact JSON 定义。您可以将文件放在src/test/resources/contracts文件夹。记得把spring-cloud-contract-pact依赖项。以下示例显示了这样的 Pact 合约:
{
"provider": {
"name": "Provider"
},
"consumer": {
"name": "Consumer"
},
"interactions": [
{
"description": "",
"request": {
"method": "PUT",
"path": "/pactfraudcheck",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"clientId": "1234567890",
"loanAmount": 99999
},
"generators": {
"body": {
"$.clientId": {
"type": "Regex",
"regex": "[0-9]{10}"
}
}
},
"matchingRules": {
"header": {
"Content-Type": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "application/json.*"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
},
"body": {
"$.clientId": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "[0-9]{10}"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
}
}
},
"response": {
"status": 200,
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"fraudCheckStatus": "FRAUD",
"rejection.reason": "Amount too high"
},
"matchingRules": {
"header": {
"Content-Type": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "application/json.*"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
},
"body": {
"$.fraudCheckStatus": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "FRAUD"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
}
}
}
}
],
"metadata": {
"pact-specification": {
"version": "3.0.0"
},
"pact-jvm": {
"version": "3.5.13"
}
}
}7.4. 生产者协议
在生产者方面,您必须向插件添加两个额外的依赖项 配置。一个是 Spring Cloud Contract Pact 支持,另一个表示 您使用的当前 Pact 版本。下面的清单显示了如何对两者执行此作 Maven 和 Gradle:
// if additional dependencies are needed e.g. for Pact
classpath "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-contract-pact:${findProperty('verifierVersion') ?: verifierVersion}"当您执行应用程序的构建时,将生成测试和存根。以下内容 example 显示了来自此进程的测试和存根:
@Test
public void validate_shouldMarkClientAsFraud() throws Exception {
// given:
MockMvcRequestSpecification request = given()
.header("Content-Type", "application/vnd.fraud.v1+json")
.body("{\"clientId\":\"1234567890\",\"loanAmount\":99999}");
// when:
ResponseOptions response = given().spec(request)
.put("/fraudcheck");
// then:
assertThat(response.statusCode()).isEqualTo(200);
assertThat(response.header("Content-Type")).matches("application/vnd\\.fraud\\.v1\\+json.*");
// and:
DocumentContext parsedJson = JsonPath.parse(response.getBody().asString());
assertThatJson(parsedJson).field("['rejectionReason']").isEqualTo("Amount too high");
// and:
assertThat(parsedJson.read("$.fraudCheckStatus", String.class)).matches("FRAUD");
}{
"id" : "996ae5ae-6834-4db6-8fac-358ca187ab62",
"uuid" : "996ae5ae-6834-4db6-8fac-358ca187ab62",
"request" : {
"url" : "/fraudcheck",
"method" : "PUT",
"headers" : {
"Content-Type" : {
"matches" : "application/vnd\\.fraud\\.v1\\+json.*"
}
},
"bodyPatterns" : [ {
"matchesJsonPath" : "$[?(@.['loanAmount'] = 99999)]"
}, {
"matchesJsonPath" : "$[?(@.clientId =~ /([0-9]{10})/)]"
} ]
},
"response" : {
"status" : 200,
"body" : "{\"fraudCheckStatus\":\"FRAUD\",\"rejectionReason\":\"Amount too high\"}",
"headers" : {
"Content-Type" : "application/vnd.fraud.v1+json;charset=UTF-8"
},
"transformers" : [ "response-template" ]
},
}7.5. 消费者协议
在使用者端,您必须向项目添加两个额外的依赖项 依赖。一个是 Spring Cloud Contract Pact 支持,另一个表示 您使用的当前 Pact 版本。下面的清单显示了如何对两者执行此作 Maven 和 Gradle:
7.6. 与 Pact Broker 通信
每当repositoryRootproperty 以 Pact 协议开头
(以pact://),则存根下载程序会尝试
从 Pact Broker 获取 Pact 合同定义。
之后设置的任何内容pact://解析为 Pact Broker URL。
通过设置环境变量、系统属性或设置的属性 在 Plugin 或 Contract 存储库配置中,您可以 调整 Downloader 的行为。下表描述了 性能:
属性的名称 |
默认值 |
描述 |
* * * |
Host from URL 传递到 |
Pact Broker 的 URL。 |
* * * |
从 URL 传递到的端口 |
Pact Broker 的端口。 |
* * * |
从 URL 传递到的协议 |
Pact Broker 的协议。 |
* * * |
存根的版本,或 |
应该用于获取存根的标记。 |
* * * |
|
应用于连接到 Pact Broker 的身份验证类型。 |
* * * |
传递给 |
连接到 Pact Broker 时使用的用户名。 |
* * * |
传递给 |
连接到 Pact Broker 时使用的密码。 |
* * * |
false |
什么时候 |
7.7. 流:使用 Pact Broker 的消费者契约方法 |消费者端
使用者使用 Pact 框架生成 Pact 文件。这 Pact 文件将发送到 Pact Broker。您可以在此处找到此类设置的示例。
7.8. 流:在生产者端使用 Pact Broker 的消费者合同方法
为了让创建者使用 Pact Broker 中的 Pact 文件,我们可以重用
我们用于外部合约的机制相同。我们路由 Spring Cloud Contract
将 Pact 实现与包含
这pact://协议。您可以将 URL 传递给
Pact 经纪人。您可以在此处找到此类设置的示例。
以下清单显示了 Maven 和 Gradle 的配置详细信息:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- Base class mappings etc. -->
<!-- We want to pick contracts from a Git repository -->
<contractsRepositoryUrl>pact://http://localhost:8085</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<!-- We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts -->
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<!-- When + is passed, a latest tag will be applied when fetching pacts -->
<version>+</version>
</contractDependency>
<!-- The contracts mode can't be classpath -->
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
</configuration>
<!-- Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath! -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-pact</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>buildscript {
repositories {
//...
}
dependencies {
// ...
// Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath!
classpath "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-contract-pact:${contractVersion}"
}
}
contracts {
// When + is passed, a latest tag will be applied when fetching pacts
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:+"
}
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "pact://http://localhost:8085"
}
// The mode can't be classpath
contractsMode = "REMOTE"
// Base class mappings etc.
}使用这样的设置:
-
Pact 文件从 Pact Broker 下载。
-
Spring Cloud Contract 将 Pact 文件转换为测试和存根。
-
像往常一样,带有存根的 JAR 会自动创建。
7.9. 流程:消费者端使用 Pact 的生产者合约方法
在不想采用消费者契约方法的情况下 (对于每个消费者,定义期望)但您更喜欢 要执行 producer 合约(producer 提供 Contract 和 publishes stubs),则可以将 Spring Cloud Contract 与 Stub Runner 选项。您可以在此处找到此类设置的示例。
请记住添加 Stub Runner 和 Spring Cloud Contract Pact 模块 作为测试依赖项。
以下清单显示了 Maven 和 Gradle 的配置详细信息:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<!-- Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath! -->
<dependencies>
<!-- ... -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-pact</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
dependencies {
//...
testCompile("org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner")
// Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath!
testCompile("org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-contract-pact")
}接下来,您可以将 Pact Broker 的 URL 传递给repositoryRoot前缀
跟pact://协议(例如pact://http://localhost:8085),如下所示
示例显示:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(stubsMode = StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE,
ids = "com.example:beer-api-producer-pact",
repositoryRoot = "pact://http://localhost:8085")
public class BeerControllerTest {
//Inject the port of the running stub
@StubRunnerPort("beer-api-producer-pact") int producerPort;
//...
}使用这样的设置:
-
Pact 文件从 Pact Broker 下载。
-
Spring Cloud Contract 将 Pact 文件转换为存根定义。
-
存根服务器将启动并馈送存根。
8. 如何调试生成的测试客户端发送的请求/响应?
生成的测试都以某种形式或方式归结为 RestAssured。放心 依赖于 Apache HttpClient。 HttpClient 有一个叫做线路日志记录的工具。 它将整个请求和响应记录到 HttpClient。Spring Boot 具有用于执行此类作的 logging 通用应用程序属性。要使用它,请将此代码添加到您的应用程序属性中,如下所示:
logging.level.org.apache.http.wire=DEBUG9. 如何调试 WireMock 发送的映射、请求或响应?
从版本开始1.2.0,我们将 WireMock 日志记录用于info并将 WireMock 通知程序设置为 verbose。现在您可以
确切地知道 WireMock 服务器收到了什么请求以及哪个请求
选择了匹配的响应定义。
要关闭此功能,请将 WireMock 日志记录设置为ERROR如下:
logging.level.com.github.tomakehurst.wiremock=ERROR10. 如何查看在 HTTP 服务器存根中注册的内容?
您可以使用mappingsOutputFolder属性@AutoConfigureStubRunner,StubRunnerRule或
'StubRunnerExtension'转储每个工件 ID 的所有映射。还有给定存根服务器的端口
已启动。
11. 如何从文件中引用文本?
在 1.2.0 版本中,我们添加了此功能。您可以调用file(…)方法中的
DSL 并提供相对于合约所在位置的路径。
如果您使用 YAML,则可以使用bodyFromFile财产。
12. 如何从 Spring Cloud Contract Contract 生成 Pact、YAML 或 X 文件?
Spring Cloud Contract 附带一个ToFileContractsTransformer类,它允许您转储
contracts 作为给定ContractConverter.它包含一个static void main方法,该方法允许您将转换器作为可执行文件执行。它需要以下内容
参数:
-
参数 1 :
FQN:的完全限定名称ContractConverter(例如,PactContractConverter).必需。 -
参数 2 :
path:应存储转储文件的路径。OPTIONAL — 默认为target/converted-contracts. -
参数 3 :
path:应搜索合同的路径。OPTIONAL — 默认为src/test/resources/contracts.
执行转换器后,将处理 Spring Cloud Contract 文件,并且
取决于提供的 FQNContractTransformer,则合同将转换
转换为所需的格式并转储到提供的文件夹中。
以下示例显示了如何为 Maven 和 Gradle 配置 Pact 集成:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.6.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>convert-dsl-to-pact</id>
<phase>process-test-classes</phase>
<configuration>
<classpathScope>test</classpathScope>
<mainClass>
org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.util.ToFileContractsTransformer
</mainClass>
<arguments>
<argument>
org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.spec.pact.PactContractConverter
</argument>
<argument>${project.basedir}/target/pacts</argument>
<argument>
${project.basedir}/src/test/resources/contracts
</argument>
</arguments>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>java</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>task convertContracts(type: JavaExec) {
main = "org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.util.ToFileContractsTransformer"
classpath = sourceSets.test.compileClasspath
args("org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.spec.pact.PactContractConverter",
"${project.rootDir}/build/pacts", "${project.rootDir}/src/test/resources/contracts")
}
test.dependsOn("convertContracts")13. 如何使用传递依赖项?
Spring Cloud Contract 插件添加了为您创建存根 jar 的任务。一 出现的问题是,在重用存根时,您可能会错误地导入所有 该存根的依赖项。在构建 Maven 工件时,即使您有几个 不同的 jar 中,它们都共享一个 POM,如下面的清单所示:
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075506-1-stubs.jar
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075506-1-stubs.jar.sha1
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075655-2-stubs.jar
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075655-2-stubs.jar.sha1
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT.jar
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT.pom
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT-stubs.jar
├── ...
└── ...有三种可能性可以使用这些依赖项,以免有任何依赖项 传递依赖项的问题:
-
将所有应用程序依赖项标记为可选
-
为 stub 创建单独的 artifactid
-
排除 Consumer 端的依赖项
13.1. 如何将所有应用程序依赖项标记为可选?
如果,在producerapplication 中,您将所有依赖项标记为可选,
当您包含producerstubs 中的存根(或当
dependency 由 Stub Runner 下载),那么,因为所有的依赖项都是
可选,则不会下载它们。
13.2. 如何创建单独的artifactid对于 Stubs?
如果您创建单独的artifactid,您可以按所需的任何方式进行设置。
例如,您可能决定完全没有依赖项。
13.3. 如何排除 Consumer 端的依赖项?
作为使用者,如果您将 stub 依赖项添加到 Classpath 中,则可以显式排除不需要的依赖项。
14. 如何从 Contract 生成 Spring REST Docs 片段?
当您希望使用 Spring REST Docs 包含 API 的请求和响应时, 如果您使用的是 MockMvc 和 RestAssuredMockMvc,则只需对设置进行一些细微的更改。 为此,请包括以下依赖项(如果尚未这样做):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-verifier</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.restdocs</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-restdocs-mockmvc</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>testImplementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-contract-verifier'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.restdocs:spring-restdocs-mockmvc'接下来,您需要对基类进行一些更改。以下示例使用WebAppContext以及 RestAssure 的独立选项:
package com.example.fraud;
import io.restassured.module.mockmvc.RestAssuredMockMvc;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Rule;
import org.junit.rules.TestName;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.restdocs.JUnitRestDocumentation;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.document;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.documentationConfiguration;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public abstract class FraudBaseWithWebAppSetup {
private static final String OUTPUT = "target/generated-snippets";
@Rule
public JUnitRestDocumentation restDocumentation = new JUnitRestDocumentation(OUTPUT);
@Rule
public TestName testName = new TestName();
@Autowired
private WebApplicationContext context;
@Before
public void setup() {
RestAssuredMockMvc.mockMvc(MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(this.context)
.apply(documentationConfiguration(this.restDocumentation))
.alwaysDo(document(
getClass().getSimpleName() + "_" + testName.getMethodName()))
.build());
}
protected void assertThatRejectionReasonIsNull(Object rejectionReason) {
assert rejectionReason == null;
}
}package com.example.fraud;
import io.restassured.module.mockmvc.RestAssuredMockMvc;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Rule;
import org.junit.rules.TestName;
import org.springframework.restdocs.JUnitRestDocumentation;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.document;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.documentationConfiguration;
public abstract class FraudBaseWithStandaloneSetup {
private static final String OUTPUT = "target/generated-snippets";
@Rule
public JUnitRestDocumentation restDocumentation = new JUnitRestDocumentation(OUTPUT);
@Rule
public TestName testName = new TestName();
@Before
public void setup() {
RestAssuredMockMvc.standaloneSetup(MockMvcBuilders
.standaloneSetup(new FraudDetectionController())
.apply(documentationConfiguration(this.restDocumentation))
.alwaysDo(document(
getClass().getSimpleName() + "_" + testName.getMethodName())));
}
}| 您无需为生成的代码片段指定输出目录(自 Spring REST Docs 版本 1.2.0.RELEASE 起)。 |
15. 如何使用某个位置的存根
如果您想从给定位置获取合约或存根而不克隆存储库或获取 JAR,只需使用stubs://协议。您可以在文档的此部分阅读有关此内容的更多信息。
16. 如何在运行时生成存根
如果你想在运行时为 Contract 生成存根,只需将generateStubs属性在@AutoConfigureStubRunner注解,或调用withGenerateStubs(true)方法。您可以在文档的此部分阅读有关此内容的更多信息。
17. 如果没有合约或存根,我该如何使构建通过。
如果您希望 Stub Runner 在未找到 stub 时不会失败,则只需将generateStubs属性在@AutoConfigureStubRunner注解,或调用withFailOnNoStubs(false)方法。您可以在文档的此部分阅读有关此内容的更多信息。
如果你希望插件在未找到 Contract 时不会使构建失败,你可以设置failOnNoStubs标志或调用contractRepository { failOnNoStubs(false) }Gradle 中的闭包。
18. 如何标记合同正在进行中
如果 Contract 正在进行中,则意味着不会生成 on the producer 端测试,但会生成存根。您可以在文档的此部分阅读有关此内容的更多信息。
在 CI 构建中,在投入生产之前,您希望确保 Classpath 上没有正在进行的 Contract。那是因为你可能会导致误报。这就是为什么默认情况下,在 Spring Cloud Contract 插件中,我们将failOnInProgress自true.如果要在生成测试时允许此类 Contract,只需将标志设置为false.