|
This version is still in development and is not considered stable yet. For the latest stable version, please use spring-cloud-function 4.1.4! |
AWS Lambda
The AWS adapter takes a Spring Cloud Function app and converts it to a form that can run in AWS Lambda.
The details of how to get started with AWS Lambda is out of scope of this document, so the expectation is that user has some familiarity with AWS and AWS Lambda and wants to learn what additional value spring provides.
Getting Started
One of the goals of Spring Cloud Function framework is to provide necessary infrastructure elements to enable a simple function application to interact in a certain way in a particular environment. A simple function application (in context or Spring) is an application that contains beans of type Supplier, Function or Consumer. So, with AWS it means that a simple function bean should somehow be recognised and executed in AWS Lambda environment.
Let’s look at the example:
@SpringBootApplication
public class FunctionConfiguration {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FunctionConfiguration.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Function<String, String> uppercase() {
return value -> value.toUpperCase();
}
}It shows a complete Spring Boot application with a function bean defined in it. What’s interesting is that on the surface this is just another boot app, but in the context of AWS Adapter it is also a perfectly valid AWS Lambda application. No other code or configuration is required. All you need to do is package it and deploy it, so let’s look how we can do that.
To make things simpler we’ve provided a sample project ready to be built and deployed and you can access it here.
You simply execute ./mvnw clean package to generate JAR file. All the necessary maven plugins have already been setup to generate
appropriate AWS deployable JAR file. (You can read more details about JAR layout in Notes on JAR Layout).
Then you have to upload the JAR file (via AWS dashboard or AWS CLI) to AWS.
When asked about handler you specify org.springframework.cloud.function.adapter.aws.FunctionInvoker::handleRequest which is a generic request handler.
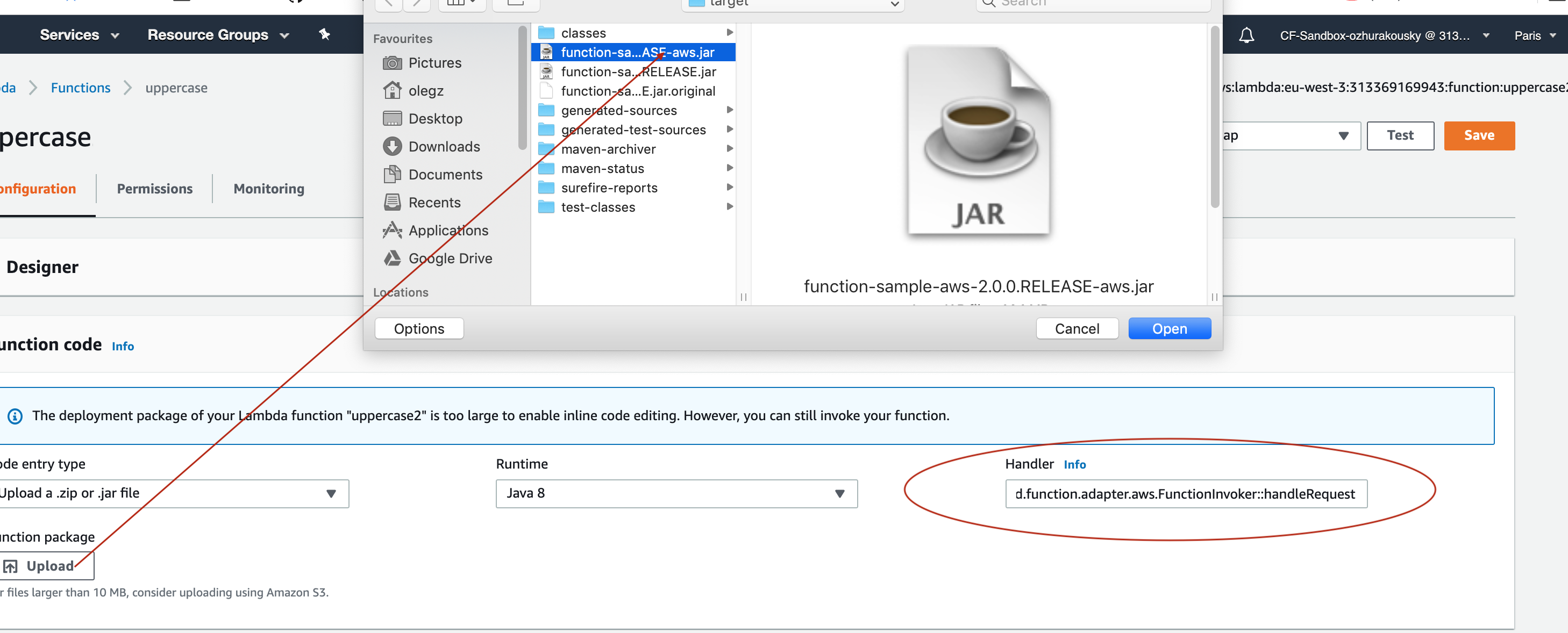
That is all. Save and execute the function with some sample data which for this function is expected to be a String which function will uppercase and return back.
While org.springframework.cloud.function.adapter.aws.FunctionInvoker is a general purpose AWS’s RequestHandler implementation aimed at completely
isolating you from the specifics of AWS Lambda API, for some cases you may want to specify which specific AWS’s RequestHandler you want
to use. The next section will explain you how you can accomplish just that.
AWS Request Handlers
While AWS Lambda allows you to implement various RequestHandlers, with Spring Cloud Function you don’t need to implement any, and instead use the provided
org.springframework.cloud.function.adapter.aws.FunctionInvoker which is the implementation of AWS’s RequestStreamHandler.
User doesn’t need to do anything other then specify it as 'handler' on AWS dashboard when deploying function.
It will handle most of the cases including Kinesis, streaming etc.
If your app has more than one @Bean of type Function etc. then you can choose the one to use by configuring spring.cloud.function.definition
property or environment variable. The functions are extracted from the Spring Cloud FunctionCatalog. In the event you don’t specify spring.cloud.function.definition
the framework will attempt to find a default following the search order where it searches first for Function then Consumer and finally Supplier).
Type Conversion
Spring Cloud Function will attempt to transparently handle type conversion between the raw input stream and types declared by your function.
For example, if your function signature is as such Function<Foo, Bar> we will attempt to convert
incoming stream event to an instance of Foo.
In the event type is not known or can not be determined (e.g., Function<?, ?>) we will attempt to
convert an incoming stream event to a generic Map.
Raw Input
There are times when you may want to have access to a raw input. In this case all you need is to declare your
function signature to accept InputStream. For example, Function<InputStream, ?>. In this case
we will not attempt any conversion and will pass the raw input directly to a function.
AWS Function Routing
One of the core features of Spring Cloud Function is routing - an ability to have one special function to delegate to other functions based on the user provided routing instructions.
In AWS Lambda environment this feature provides one additional benefit, as it allows you to bind a single function (Routing Function) as AWS Lambda and thus a single HTTP endpoint for API Gateway. So in the end you only manage one function and one endpoint, while benefiting from many function that can be part of your application.
More details are available in the provided sample, yet few general things worth mentioning.
Routing capabilities will be enabled by default whenever there is more then one function in your application as org.springframework.cloud.function.adapter.aws.FunctionInvoker
can not determine which function to bind as AWS Lambda, so it defaults to RoutingFunction.
This means that all you need to do is provide routing instructions which you can do using several mechanisms
(see sample for more details).
Also, note that since AWS does not allow dots . and/or hyphens`-` in the name of the environment variable, you can benefit from boot support and simply substitute
dots with underscores and hyphens with camel case. So for example spring.cloud.function.definition becomes spring_cloud_function_definition
and spring.cloud.function.routing-expression becomes spring_cloud_function_routingExpression.
Custom Runtime
You can also benefit from AWS Lambda custom runtime feature of AWS Lambda and Spring Cloud Function provides all the necessary components to make it easy.
From the code perspective the application should look no different then any other Spring Cloud Function application.
The only thing you need to do is to provide a bootstrap script in the root of your zip/jar that runs the Spring Boot application.
and select "Custom Runtime" when creating a function in AWS.
Here is an example 'bootstrap' file:
#!/bin/sh
cd ${LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT:-.}
java -Dspring.main.web-application-type=none -Dspring.jmx.enabled=false \
-noverify -XX:TieredStopAtLevel=1 -Xss256K -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=128M \
-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom \
-cp .:`echo lib/*.jar | tr ' ' :` com.example.LambdaApplicationThe com.example.LambdaApplication represents your application which contains function beans.
Set the handler name in AWS to the name of your function. You can use function composition here as well (e.g., uppercase|reverse).
That is pretty much all. Once you upload your zip/jar to AWS your function will run in custom runtime.
We provide a sample project
where you can also see how to configure your POM to properly generate the zip file.
The functional bean definition style works for custom runtimes as well, and is
faster than the @Bean style. A custom runtime can start up much quicker even than a functional bean implementation
of a Java lambda - it depends mostly on the number of classes you need to load at runtime.
Spring doesn’t do very much here, so you can reduce the cold start time by only using primitive types in your function, for instance,
and not doing any work in custom @PostConstruct initializers.
AWS Function Routing with Custom Runtime
When using Custom Runtime Function Routing works the same way. All you need is to specify functionRouter as AWS Handler the same way you would use the name of the function as handler.
Deploying Container images
Custom Runtime is also responsible for handling of container image deployments.
When deploying container images in a way similar to the one described here, it is important
to remember to set and environment variable DEFAULT_HANDLER with the name of the function.
For example, for function bean shown below the DEFAULT_HANDLER value would be readMessageFromSQS.
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SQSMessageEvent>> readMessageFromSQS() {
return incomingMessage -> {..}
}Also, it is important to remember to ensure tht spring_cloud_function_web_export_enabled is also set to false. It is by default.
Notes on JAR Layout
You don’t need the Spring Cloud Function Web or Stream adapter at runtime in Lambda, so you might
need to exclude those before you create the JAR you send to AWS. A Lambda application has to be
shaded, but a Spring Boot standalone application does not, so you can run the same app using 2
separate jars (as per the sample). The sample app creates 2 jar files, one with an aws
classifier for deploying in Lambda, and one executable (thin) jar that includes spring-cloud-function-web
at runtime. Spring Cloud Function will try and locate a "main class" for you from the JAR file
manifest, using the Start-Class attribute (which will be added for you by the Spring Boot
tooling if you use the starter parent). If there is no Start-Class in your manifest you can
use an environment variable or system property MAIN_CLASS when you deploy the function to AWS.
If you are not using the functional bean definitions but relying on Spring Boot’s auto-configuration,
and are not depending on spring-boot-starter-parent,
then additional transformers must be configured as part of the maven-shade-plugin execution.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<createDependencyReducedPom>false</createDependencyReducedPom>
<shadedArtifactAttached>true</shadedArtifactAttached>
<shadedClassifierName>aws</shadedClassifierName>
<transformers>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.AppendingTransformer">
<resource>META-INF/spring.handlers</resource>
</transformer>
<transformer implementation="org.springframework.boot.maven.PropertiesMergingResourceTransformer">
<resource>META-INF/spring.factories</resource>
</transformer>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.AppendingTransformer">
<resource>META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports</resource>
</transformer>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.AppendingTransformer">
<resource>META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.ManagementContextConfiguration.imports</resource>
</transformer>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.AppendingTransformer">
<resource>META-INF/spring.schemas</resource>
</transformer>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.AppendingTransformer">
<resource>META-INF/spring.components</resource>
</transformer>
</transformers>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>Build file setup
In order to run Spring Cloud Function applications on AWS Lambda, you can leverage Maven or Gradle plugins offered by the cloud platform provider.
Maven
In order to use the adapter plugin for Maven, add the plugin dependency to your pom.xml
file:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-function-adapter-aws</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>As pointed out in the Notes on JAR Layout, you will need a shaded jar in order to upload it to AWS Lambda. You can use the Maven Shade Plugin for that. The example of the setup can be found above.
You can use the Spring Boot Maven Plugin to generate the thin jar.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot.experimental</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-thin-layout</artifactId>
<version>${wrapper.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>You can find the entire sample pom.xml file for deploying Spring Cloud Function
applications to AWS Lambda with Maven here.
Gradle
In order to use the adapter plugin for Gradle, add the dependency to your build.gradle file:
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-function-adapter-aws:${version}")
}As pointed out in Notes on JAR Layout, you will need a shaded jar in order to upload it to AWS Lambda. You can use the Gradle Shadow Plugin for that:
You can use the Spring Boot Gradle Plugin and Spring Boot Thin Gradle Plugin to generate the thin jar.
Below is a complete gradle file
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.0-M2'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.3'
id 'com.github.johnrengelman.shadow' version '8.1.1'
id 'maven-publish'
id 'org.springframework.boot.experimental.thin-launcher' version "1.0.31.RELEASE"
}
group = 'com.example'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
java {
sourceCompatibility = '17'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
mavenLocal()
maven { url 'https://repo.spring.io/milestone' }
}
ext {
set('springCloudVersion', "2023.0.0-M1")
}
assemble.dependsOn = [thinJar, shadowJar]
publishing {
publications {
maven(MavenPublication) {
from components.java
versionMapping {
usage('java-api') {
fromResolutionOf('runtimeClasspath')
}
usage('java-runtime') {
fromResolutionResult()
}
}
}
}
}
shadowJar.mustRunAfter thinJar
import com.github.jengelman.gradle.plugins.shadow.transformers.*
shadowJar {
archiveClassifier = 'aws'
manifest {
inheritFrom(project.tasks.thinJar.manifest)
}
// Required for Spring
mergeServiceFiles()
append 'META-INF/spring.handlers'
append 'META-INF/spring.schemas'
append 'META-INF/spring.tooling'
append 'META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports'
append 'META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.web.ManagementContextConfiguration.imports'
transform(PropertiesFileTransformer) {
paths = ['META-INF/spring.factories']
mergeStrategy = "append"
}
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter'
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-function-adapter-aws'
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-function-context'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}You can find the entire sample build.gradle file for deploying Spring Cloud Function
applications to AWS Lambda with Gradle here.